Code
Add your own Python code to a pipeline in a fast and easy way. The code is instantly validated when you enter it in the code parameter.
Basic Information
- Type:
deepset_cloud_custom_nodes.code.code_component.Code - Components it can connect with:
- Any component whose inputs and outputs match the custom component you declare in the
codeparameter.
- Any component whose inputs and outputs match the custom component you declare in the
Inputs and Outputs
You define the component's inputs and outputs in its run() method. Make sure their types match the input and output types of the components you want to connect to.
Overview
Use Code as a fast way to add your own code to a pipeline. It's a good choice if:
- The code is only usable in a single pipeline
- You don't want to share the code with the whole organization
- Your code doesn't have external dependencies or rely on external libraries
- You don't need to version or test the code with CI/CD
Otherwise, consider creating a custom component. For more information, see Custom Components.
Component's Structure
Each component is a Python class with the following required elements:
- The
from haystack import componentimport statement. - The
@componentdecorator to indicate you're creating a component. - The
run()method that defines what the component does.- The
run()method must have the@component.output_typesdecorator to define the type of data the component outputs and the name of the outputting edge. The names and types you define as output types must match the keys and value types of the dictionary object therun()method returns. For details, see Examples below. - You can specify the input parameters for the
run()method. - The
run()method must return a dictionary with the keys and values you specify.
- The
Restrictions
The init() method must not have any parameters.
You can use the AI assistant to generate code for your Code component. To do this, click the AI Assistant button on the component card and write your request in the prompt.
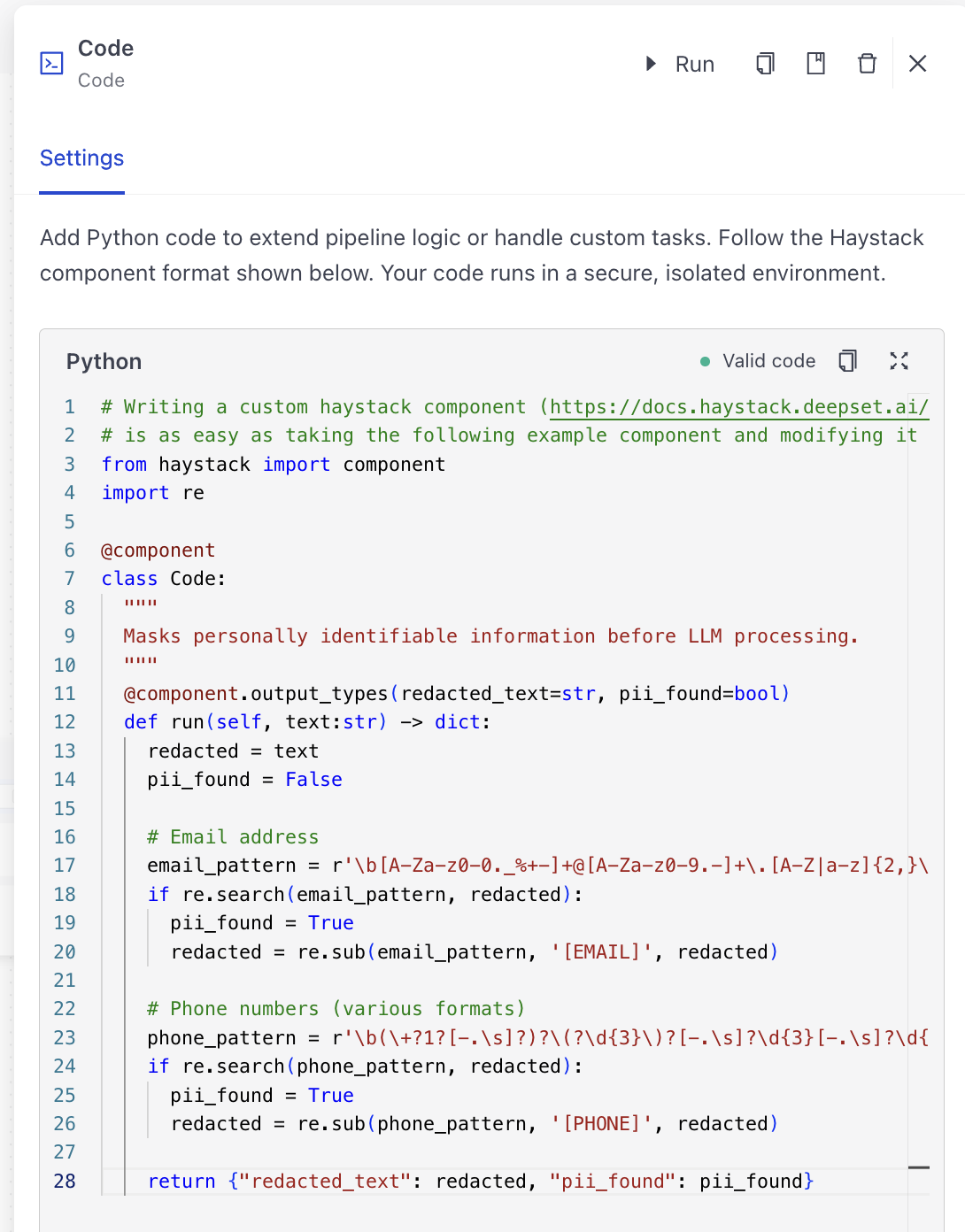
Usage Example
This is a query pipeline that masks sensitive information, like emails or phone numbers, before sending the data to an LLM. pii_redactor is a Code component with custom Python code that masks the sensitive information.
components:
pii_redactor:
type: deepset_cloud_custom_nodes.code.code_component.Code
init_parameters:
code: |
import re
from haystack import component
@component
class Code:
"""Masks personally identifiable information before LLM processing."""
@component.output_types(redacted_text=str, pii_found=bool)
def run(self, text: str) -> dict:
redacted = text
pii_found = False
# Email addresses
email_pattern = r'\b[A-Za-z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\.[A-Z|a-z]{2,}\b'
if re.search(email_pattern, redacted):
pii_found = True
redacted = re.sub(email_pattern, '[EMAIL]', redacted)
# Phone numbers (various formats)
phone_pattern = r'\b(\+?1?[-.\s]?)?\(?\d{3}\)?[-.\s]?\d{3}[-.\s]?\d{4}\b'
if re.search(phone_pattern, redacted):
pii_found = True
redacted = re.sub(phone_pattern, '[PHONE]', redacted)
return {"redacted_text": redacted, "pii_found": pii_found}
prompt_builder:
type: haystack.components.builders.prompt_builder.PromptBuilder
init_parameters:
template: |
Help the user with their request: {{ query }}
llm:
type: haystack.components.generators.openai.OpenAIGenerator
init_parameters:
model: gpt-4o-mini
api_key:
type: env_var
env_vars:
- OPENAI_API_KEY
strict: false
answer_builder:
type: haystack.components.builders.answer_builder.AnswerBuilder
init_parameters: {}
connections:
- sender: pii_redactor.redacted_text
receiver: prompt_builder.query
- sender: prompt_builder.prompt
receiver: llm.prompt
- sender: llm.replies
receiver: answer_builder.replies
inputs:
query:
- answer_builder.query
- pii_redactor.text
outputs:
answers: answer_builder.answers
max_runs_per_component: 100
metadata: {}
This is what the component looks like in the Builder:
Testing the Code
Your code is validated as you type it in the code parameter. If there are any errors, you'll see a red error message in the code parameter.
To test your code, click Run on the component card. Provide the component input and click Run Component. You should see the component's outputs in the Results panel.
Parameters
Init Parameters
These parameters are available in Pipeline Builder.
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| code | str | Python source that defines exactly one class decorated with @component. The class must not add custom __init__ parameters and must expose a run() method. |
Run Method Parameters
These parameters are available at query time through the API, Playground, or jobs.
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inputs defined in your code | Dynamic | Inherited from the wrapped component | Whatever arguments your inline component declares become keyword arguments for run(). Set them the same way you would configure any other component parameter. |
Troubleshooting
- "No Haystack component found" error: Add the
@componentdecorator to your class and keep only one component definition inside thecodestring. - "Component has init parameters" error: Remove every parameter from the custom class
__init__. Move configuration into class attributes orrun()parameters instead. - Type errors during
run(): Ensure upstream nodes send the exact data types your inline component expects. Mismatched socket names or missing keyword arguments raiseTypeErrorbecauseCodeforwards inputs directly to the wrapped component.
Performance Considerations
Codeexecutes your snippet once during pipeline load, so heavy imports or long module-level logic slow down startup but not per-request execution.- The inline component runs synchronously with the rest of the pipeline. Complex logic in
run()increases latency in lockstep. - Treat the
codefield like executable configuration. Store only trusted code and monitor version control changes to keep track of what runs inside your pipelines.
Was this page helpful?