Agent
Add reasoning and external tools to your pipelines through the Agent component.
Basic Information
- Type:
haystack.components.agents.agent.Agent - Components it can connect with:
- To pass a query to an Agent, use
OutputAdapter,DeepsetChatHistoryParser, orChatPromptBuilder.ChatPromptBuilderalso lets you pass dynamic content to the Agent. - To make the Agent's response the final output of your pipeline, use an
OutputAdapterto convert the Agent's messages into a list of strings and send them on toAnswerBuilder. - The connections depend on the output and input types configured in the Agent's
state_schema.
- To pass a query to an Agent, use
Inputs
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| messages | List[ChatMessage] | List of Haystack ChatMessage objects to process. If a list of dictionaries is provided, each dictionary is converted into a ChatMessage object. | |
| streaming_callback | Optional[StreamingCallbackT] | None | A callback function to invoke when a response is streamed from the LLM. You can configure the same callback function for emitting tool results when the agent calls a tool. |
| system_prompt | Optional[str] | None | System prompt for this specific run. If provided, it overrides the default system prompt configured during initialization. This allows you to dynamically adjust the Agent's behavior for different queries. |
| tools | Optional[Union[List[Tool], Toolset, List[str]]] | None | Optional list of Tool objects, a Toolset, or list of tool names to use for this run. When passing tool names, tools are selected from the Agent's originally configured tools. This allows you to dynamically select which tools the Agent uses at query time. |
| kwargs | Any | Additional inputs forwarded to the Agent's state. The keys must match the schema defined in the Agent's state_schema. |
Outputs
| Output | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| messages | List[ChatMessage] | Complete conversation history including all messages from the Agent run: user messages, LLM responses, tool calls, and tool results. |
| last_message | ChatMessage | The final message from the Agent run, typically containing the LLM's final response. This is useful when you only need the final result. |
| Additional state outputs | Varies | Any fields defined in state_schema are also returned as outputs (for example, documents, repository). |
Unlike a ChatGenerator, which returns only the final message, the Agent returns all messages generated during the process. This includes the messages provided as input.|
Overview
Agent is designed to help AI systems use tools to accomplish tasks. You can think of it like a coordinator that manages conversations and knows when and how to use different tools.
Key features:
- Works with different language models.
You can configure the model through an underlyingChatGenerator. - Can use external tools.
The tools include entire pipelines, custom functions, and MCP servers. - Lets you define custom exit conditions.
Exit conditions specify when the Agent should stop, for example, after generating text or using a specific tool. - Maintains conversation history.
The Agent keeps track of events during a single interaction. To maintain context across multiple queries (like in a real chat), use the Haystack Enterprise Platform Chat endpoint orDeepsetChatHistoryParser. - Allows real-time streaming responses.
Streaming is supported for both synchronous and asynchronous mode. - Supports asynchronous execution.
The Agent provides bothrun()andrun_async()methods for synchronous and asynchronous pipeline execution. - Has tracing support.
Connect a tracer like Langfuse or Weights & Biases Weave to monitor the Agent's execution in depth.
How It Works
- The Agent receives a message from the user.
- It sends the message to its chat model, along with the list of tools.
- The model decides whether it needs to call tools or can answer right away. It responds with either plain text (the final response) or a tool call.
- If the response is just text, the Agent returns the current conversation and the response.
- If the response includes a tool call:
- The Agent calls the tool and collects the result.
- If any of the tool's outputs should be stored in the Agent's state, the Agent adds the specified tool result to the state.
- The Agent adds the result to the conversation history.
- Then:
- If the tool name matches an item of the
exit_conditionslist AND the tool executed successfully without errors, the Agent exits and returns the conversation. If the tool produced an error, the Agent continues and sends the error message back to the LLM. - If it doesn't match, the Agent continues. It sends the updated conversation back to the model. The model may decide to call another tool or the same one again. This loop continues until one of the
exit_conditionsis met ormax_agent_stepsis reached.
- If the tool name matches an item of the
Configuration
To configure an Agent, provide:
- A model that supports tool calls: The Agent is provider-agnostic, so it can work with any model.
- A list of tools: These can be custom tools for a specific use case, pipeline components, entire pipelines, or MCP tools.
- Optionally, add a system prompt to provide fixed instructions that guide the agent's behavior, tone, or knowledge throughout the conversation. The system prompt only supports static content. It's plain text. For detailed instructions on writing prompts and adding dynamic content to system prompts, see Writing Prompts in Haystack Enterprise Platform.
- Optionally, add a user prompt with a reusable Jinja2 template. This lets you invoke the Agent with dynamic variables without manually constructing
ChatMessageobjects. When you combinemessageswithuser_prompt, the rendered user prompt is appended to the provided messages. Userequired_variablesto specify which template variables must be provided.
On the Advanced tab, you can also configure model-specific settings and agent-specific settings, which include:
- Max agent steps to limit the number of actions the agent can perform. For more complicated tasks, you may need to increase this value. Note that increasing this value may increase the cost and time of the task.
- Exit conditions to define when the agent stops. The Agent runs iteratively, calling tools and feeding their outputs back to the model until one of the exit conditions is met.
- To stop the agent when it generates a text response, choose
text. - To stop the agent after a specific tool is used, choose the tool's name from the list.
- You can choose multiple exit conditions and the agent stops when any of the conditions is met. For example, to stop the agent when it generates a text response or after a specific tool is used, choose
textand the tool's name.
- To stop the agent when it generates a text response, choose
- Retry on tool failure to automatically retry the agent if a tool call fails. This is useful if the tool call times out or temporarily fails.
For guidance on how to configure the Agent, see Building AI Agents.
For an explanation of the Agent and its tools, see also AI Agent and Agent Tools.
Agent Without Tools
When you initialize an Agent without providing tools, it behaves like a standard ChatGenerator:
- It produces one response from the LLM
- It immediately exits after generating text
- It cannot perform iterative reasoning or tool calling
This mode is useful for simple conversational tasks that don't require external tools.
Agent and Tools
Agents can use pipelines, components, custom functions, and MCP servers as tools. For instructions on how to configure them in Builder, see Configure an Agent.
SearchableToolset
For applications with large tool catalogs, use SearchableToolset instead of passing all tools directly. Instead of exposing all tools upfront, agents start with a single search_tools function and dynamically discover relevant tools using BM25-based keyword search. This reduces context usage and improves tool selection.
SearchableToolset is useful when connecting MCP servers through MCPToolset, where many tools may be available. By combining the two, agents load only the tools they need at runtime.
For small catalogs (below search_threshold, which defaults to eight), SearchableToolset acts as a passthrough and exposes all tools directly.
To learn more about tools, see Agent Tools.
Usage Examples
Pipeline as a Tool
This is an agent that uses internal_search (a RAG pipeline) as a tool:
components:
DeepsetChatHistoryParser:
type: deepset_cloud_custom_nodes.parsers.chat_history_parser.DeepsetChatHistoryParser
init_parameters: {}
Agent:
type: haystack.components.agents.agent.Agent
init_parameters:
chat_generator:
init_parameters:
model: gpt-5.2
type: haystack.components.generators.chat.openai_responses.OpenAIResponsesChatGenerator
tools:
- type: haystack.tools.pipeline_tool.PipelineTool
data:
name: internal_search
description: Use internal_search to search the company database and find information about the company and its processes.
input_mapping:
query:
- retriever.query
- ranker.query
- prompt_builder.question
- answer_builder.query
filters:
- retriever.filters_bm25
- retriever.filters_embedding
files:
- multi_file_converter.sources
output_mapping:
attachments_joiner.documents: documents
answer_builder.answers: answers
pipeline:
components:
retriever:
type: haystack_integrations.components.retrievers.opensearch.open_search_hybrid_retriever.OpenSearchHybridRetriever
init_parameters:
document_store:
type: haystack_integrations.document_stores.opensearch.document_store.OpenSearchDocumentStore
init_parameters:
hosts:
index: Standard-Index-English
max_chunk_bytes: 104857600
embedding_dim: 768
return_embedding: false
method:
mappings:
settings:
create_index: true
http_auth:
use_ssl:
verify_certs:
timeout:
top_k: 20
fuzziness: 0
embedder:
type: deepset_cloud_custom_nodes.embedders.nvidia.text_embedder.DeepsetNvidiaTextEmbedder
init_parameters:
normalize_embeddings: true
model: intfloat/e5-base-v2
ranker:
type: deepset_cloud_custom_nodes.rankers.nvidia.ranker.DeepsetNvidiaRanker
init_parameters:
model: intfloat/simlm-msmarco-reranker
top_k: 8
meta_field_grouping_ranker:
type: haystack.components.rankers.meta_field_grouping_ranker.MetaFieldGroupingRanker
init_parameters:
group_by: file_id
subgroup_by:
sort_docs_by: split_id
prompt_builder:
type: haystack.components.builders.prompt_builder.PromptBuilder
init_parameters:
required_variables: '*'
template: "You are a technical expert.\nYou answer questions truthfully based on provided documents.\nIf the answer exists in several documents, summarize them.\nIgnore documents that don't contain the answer to the question.\nOnly answer based on the documents provided. Don't make things up.\nIf no information related to the question can be found in the document, say so.\nAlways use references in the form [NUMBER OF DOCUMENT] when using information from a document, e.g. [3] for Document [3] .\nNever name the documents, only enter a number in square brackets as a reference.\nThe reference must only refer to the number that comes in square brackets after the document.\nOtherwise, do not use brackets in your answer and reference ONLY the number of the document without mentioning the word document.\n\nThese are the documents:\n{%- if documents|length > 0 %}\n{%- for document in documents %}\nDocument [{{ loop.index }}] :\nName of Source File: {{ document.meta.file_name }}\n{{ document.content }}\n{% endfor -%}\n{%- else %}\nNo relevant documents found.\nRespond with \"Sorry, no matching documents were found, please adjust the filters or try a different question.\"\n{% endif %}\n\nQuestion: {{ question }}\nAnswer:"
llm:
type: deepset_cloud_custom_nodes.generators.deepset_amazon_bedrock_generator.DeepsetAmazonBedrockGenerator
init_parameters:
model: us.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-20250514-v1:0
aws_region_name: us-west-2
thinking:
type: enabled
budget_tokens: 1024
max_length: 1674
answer_builder:
type: deepset_cloud_custom_nodes.augmenters.deepset_answer_builder.DeepsetAnswerBuilder
init_parameters:
reference_pattern: acm
attachments_joiner:
type: haystack.components.joiners.document_joiner.DocumentJoiner
init_parameters:
join_mode: concatenate
weights:
top_k:
sort_by_score: true
multi_file_converter:
type: haystack.core.super_component.super_component.SuperComponent
init_parameters:
input_mapping:
sources:
- file_classifier.sources
is_pipeline_async: false
output_mapping:
score_adder.output: documents
pipeline:
components:
file_classifier:
type: haystack.components.routers.file_type_router.FileTypeRouter
init_parameters:
mime_types:
- text/plain
- application/pdf
- text/markdown
- text/html
- application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document
- application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.presentation
- application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet
- text/csv
text_converter:
type: haystack.components.converters.txt.TextFileToDocument
init_parameters:
encoding: utf-8
pdf_converter:
type: haystack.components.converters.pdfminer.PDFMinerToDocument
init_parameters:
line_overlap: 0.5
char_margin: 2
line_margin: 0.5
word_margin: 0.1
boxes_flow: 0.5
detect_vertical: true
all_texts: false
store_full_path: false
markdown_converter:
type: haystack.components.converters.txt.TextFileToDocument
init_parameters:
encoding: utf-8
html_converter:
type: haystack.components.converters.html.HTMLToDocument
init_parameters:
extraction_kwargs:
output_format: markdown
target_language:
include_tables: true
include_links: true
docx_converter:
type: haystack.components.converters.docx.DOCXToDocument
init_parameters:
link_format: markdown
pptx_converter:
type: haystack.components.converters.pptx.PPTXToDocument
init_parameters: {}
xlsx_converter:
type: haystack.components.converters.xlsx.XLSXToDocument
init_parameters: {}
csv_converter:
type: haystack.components.converters.csv.CSVToDocument
init_parameters:
encoding: utf-8
splitter:
type: haystack.components.preprocessors.document_splitter.DocumentSplitter
init_parameters:
split_by: word
split_length: 250
split_overlap: 30
respect_sentence_boundary: true
language: en
score_adder:
type: haystack.components.converters.output_adapter.OutputAdapter
init_parameters:
template: "{%- set scored_documents = [] -%}\n{%- for document in documents -%}\n {%- set doc_dict = document.to_dict() -%}\n {%- set _ = doc_dict.update({'score': 100.0}) -%}\n {%- set scored_doc = document.from_dict(doc_dict) -%}\n {%- set _ = scored_documents.append(scored_doc) -%}\n{%- endfor -%}\n{{ scored_documents }}\n"
output_type: List[haystack.Document]
custom_filters:
unsafe: true
text_joiner:
type: haystack.components.joiners.document_joiner.DocumentJoiner
init_parameters:
join_mode: concatenate
sort_by_score: false
tabular_joiner:
type: haystack.components.joiners.document_joiner.DocumentJoiner
init_parameters:
join_mode: concatenate
sort_by_score: false
connections:
- sender: file_classifier.text/plain
receiver: text_converter.sources
- sender: file_classifier.application/pdf
receiver: pdf_converter.sources
- sender: file_classifier.text/markdown
receiver: markdown_converter.sources
- sender: file_classifier.text/html
receiver: html_converter.sources
- sender: file_classifier.application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document
receiver: docx_converter.sources
- sender: file_classifier.application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.presentationml.presentation
receiver: pptx_converter.sources
- sender: file_classifier.application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spreadsheetml.sheet
receiver: xlsx_converter.sources
- sender: file_classifier.text/csv
receiver: csv_converter.sources
- sender: text_joiner.documents
receiver: splitter.documents
- sender: text_converter.documents
receiver: text_joiner.documents
- sender: pdf_converter.documents
receiver: text_joiner.documents
- sender: markdown_converter.documents
receiver: text_joiner.documents
- sender: html_converter.documents
receiver: text_joiner.documents
- sender: pptx_converter.documents
receiver: text_joiner.documents
- sender: docx_converter.documents
receiver: text_joiner.documents
- sender: xlsx_converter.documents
receiver: tabular_joiner.documents
- sender: csv_converter.documents
receiver: tabular_joiner.documents
- sender: splitter.documents
receiver: tabular_joiner.documents
- sender: tabular_joiner.documents
receiver: score_adder.documents
connections:
- sender: retriever.documents
receiver: ranker.documents
- sender: ranker.documents
receiver: meta_field_grouping_ranker.documents
- sender: prompt_builder.prompt
receiver: llm.prompt
- sender: prompt_builder.prompt
receiver: answer_builder.prompt
- sender: llm.replies
receiver: answer_builder.replies
- sender: multi_file_converter.documents
receiver: attachments_joiner.documents
- sender: meta_field_grouping_ranker.documents
receiver: attachments_joiner.documents
- sender: attachments_joiner.documents
receiver: answer_builder.documents
- sender: attachments_joiner.documents
receiver: prompt_builder.documents
max_runs_per_component: 100
metadata: {}
is_pipeline_async: false
inputs_from_state: {}
outputs_to_string:
documents:
source: documents
answers:
source: answers
outputs_to_state:
documents:
source: documents
parameters:
$defs:
ByteStream:
properties:
data:
description: The binary data stored in Bytestream.
format: binary
type: string
meta:
additionalProperties: true
default: {}
description: Additional metadata to be stored with the ByteStream.
type: object
mime_type:
anyOf:
- type: string
- type: 'null'
default:
description: The mime type of the binary data.
required:
- data
type: object
description: "A component that combines: 'retriever': Runs the wrapped pipeline with the provided inputs., 'ranker': Returns a list of documents ranked by their similarity to the given query., 'prompt_builder': Renders the prompt template with the provided variables., 'answer_builder': Turns the output of a Generator into `Answer` objects using regular expressions., 'multi_file_converter': Runs the wrapped pipeline with the provided inputs."
properties:
query:
description: "Provided to the 'ranker' component as: 'The input query to compare the documents to.', and Provided to the 'answer_builder' component as: 'The query used in the prompts for the Generator.'."
type: string
filters:
additionalProperties: true
description: Input 'filters' for the component.
type: object
files:
description: Input 'files' for the component.
items:
anyOf:
- type: string
- format: path
type: string
- $ref: '#/$defs/ByteStream'
type: array
required:
- query
- files
type: object
_meta:
name: internal_search
description: Use internal_search to search the company database and find information about the company and its processes.
tool_id:
system_prompt: "You are a deep research assistant.\nYou create comprehensive research reports to answer the user's questions.\nYou use the 'internal_search' tool to answer any questions about the company and its processes.\nYou perform multiple searches until you have the information you need to answer the question.\nMake sure you research different aspects of the question.\nUse markdown to format your response.\nWhen answering, cite your sources using markdown links.\nIt is important that you cite accurately."
exit_conditions:
state_schema:
documents:
type: list[haystack.dataclasses.document.Document]
_meta:
used_by:
internal_search: output
max_agent_steps: 100
streaming_callback:
raise_on_tool_invocation_failure: false
tool_invoker_kwargs:
AnswerBuilder:
type: haystack.components.builders.answer_builder.AnswerBuilder
init_parameters:
pattern:
reference_pattern:
last_message_only: false
return_only_referenced_documents: true
connections:
- sender: DeepsetChatHistoryParser.messages
receiver: Agent.messages
- sender: Agent.messages
receiver: AnswerBuilder.replies
max_runs_per_component: 100
metadata: {}
inputs:
query:
- DeepsetChatHistoryParser.history_and_query
- AnswerBuilder.query
outputs:
answers: AnswerBuilder.answers
documents: Agent.documents
metadata:
inputs: query:
- DeepsetChatHistoryParser.history_and_query
- AnswerBuilder.query
outputs: answers: AnswerBuilder.answers documents: Agent.documents
### Passing a Query to the Agent
The Agent expects a list of messages as input. However, the `Query` component outputs plain text. To bridge this gap, you can use the `DeepsetChatHistoryParser` component.
`DeepsetChatHistoryParser` takes the text from `Query` and converts it into a list of `ChatMessage` objects. Simply connect `Query` to `DeepsetChatHistoryParser,` and then connect its output to the Agent.
<ClickableImage
src="/img/concepts/agent_with_historyparser.png"
alt="Agent connected to DeepsetChatHistoryParser in Pipeline Builder"
size="standard"
/>
### Displaying the Agent Results
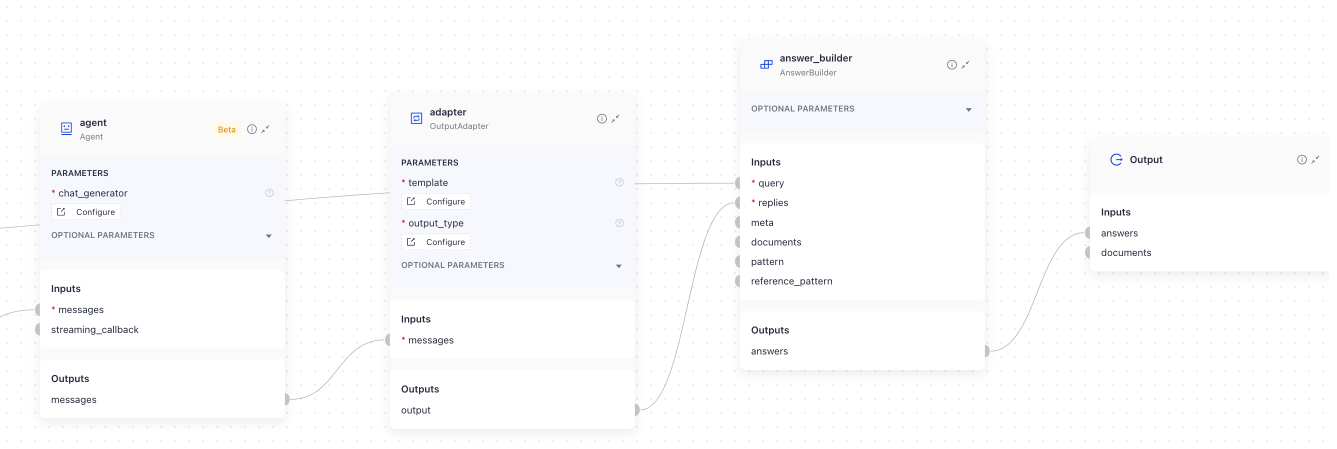
The Agent returns a list of `ChatMessages`, but in most cases, you only need the last message as the final output of your pipeline. To extract just the last message, use the `OutputAdapter` component. Configure it to:
- Take the Agent's output (a list of ChatMessages)
- Convert only the last message into a list of strings
This format is compatible with downstream components like the `AnswerBuilder`. Simply connect the Agent to the `OutputAdapter`, and then connect the adapter's output to the `AnswerBuilder`.
<ClickableImage
src="/img/concepts/agent_answerbuilder.png"
alt="Agent connected to OutputAdapter in Pipeline Builder"
size="standard"
/>
This is how to configure `OutputAdapter` for this scenario:
```yaml
adapter:
init_parameters:
output_type: List[str] # this is the output type an AnswerBuilder accepts
template: '{{ [(messages|last).text] }}' # here you're pointing to the last message the Agent returned
type: haystack.components.converters.output_adapter.OutputAdapter
Passing a Query to the Agent
The Agent expects a list of messages as input. However, the Query component outputs plain text. To bridge this gap, you can use the DeepsetChatHistoryParser component.
DeepsetChatHistoryParser takes the text from Query and converts it into a list of ChatMessage objects. Simply connect Query to DeepsetChatHistoryParser, and then connect its output to the Agent.
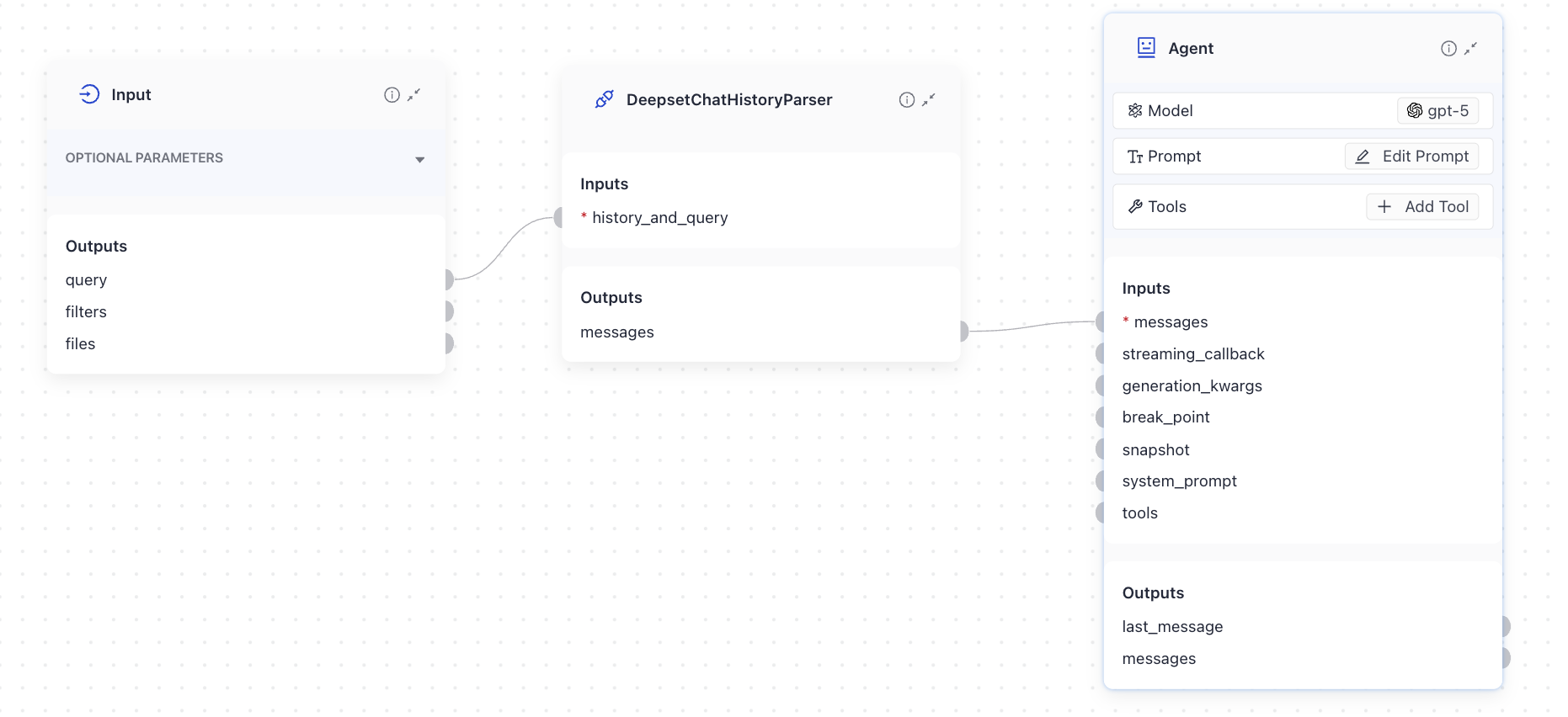
Displaying the Agent Results
The Agent returns a list of ChatMessages, but in most cases, you only need the last message as the final output of your pipeline. To extract just the last message, use the OutputAdapter component. Configure it to:
- Take the Agent's output (a list of ChatMessages)
- Convert only the last message into a list of strings
This format is compatible with downstream components like the AnswerBuilder. Simply connect the Agent to the OutputAdapter, and then connect the adapter's output to the AnswerBuilder.
This is how to configure OutputAdapter for this scenario:
adapter:
init_parameters:
output_type: List[str] # this is the output type an AnswerBuilder accepts
template: '{{ [(messages|last).text] }}' # here you're pointing to the last message the Agent returned
type: haystack.components.converters.output_adapter.OutputAdapter
Adding Sources to Agent Results
To show the sources or documents the Agent used to generate it answer, configure the Agent to output those documents. To do this, open the configuration of the tool that outputs the documents and choose to output them to State.
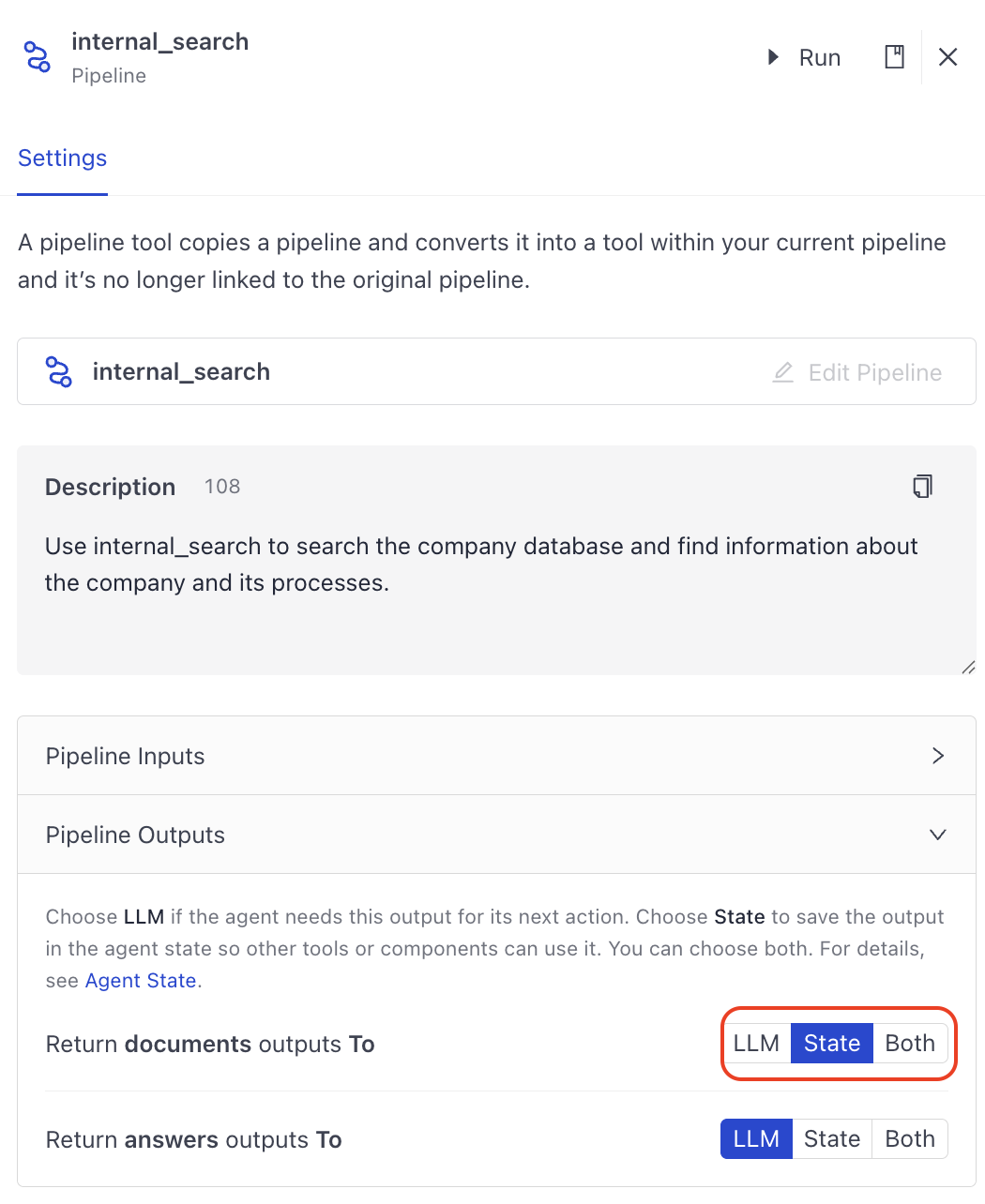
The Agent then outputs the documents through its output connection called documents. You can connect an AnswerBuilder to the Agent's documents to add documents to the final answer:
connections:
- receiver: agent.messages
sender: history_parser.messages
- receiver: adapter.messages
sender: agent.messages
- receiver: answer_builder.replies
sender: adapter.output
- sender: agent.documents # we're sending the documents to DeepsetAnswerBuilder
receiver: answer_builder.documents
inputs:
query:
- answer_builder.query
- history_parser.history_and_query
outputs:
answers: answer_builder.answers
documents: agent.documents # the final output also includes the Agent's documents
Parameters
Init Parameters
These are the parameters you can configure in Pipeline Builder:
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| chat_generator | ChatGenerator | The chat generator that the agent will use. You configure the generator by passing its init parameters and type to the Agent. Check the Usage Example section for details. The chat generator must support tools. | |
| tools | Optional[Union[List[Tool], Toolset]] | None | External tools or toolsets the Agent can use. You can provide individual Tool objects as a list, or organize related tools into a Toolset. |
| system_prompt | Optional[str] | None | System prompt to guide the Agent's behavior. This can be overridden at runtime by passing a system_prompt parameter to the run method. |
| user_prompt | Optional[str] | None | A reusable Jinja2-templated user prompt. If provided, this is rendered with the given variables and appended to the messages provided at runtime. This lets you invoke the Agent with dynamic inputs without manually constructing ChatMessage objects. Can be overridden at runtime. |
| required_variables | Optional[Union[List[str], Literal["*"]]] | None | List of variables that must be provided as input to user_prompt. If a required variable is not provided, an exception is raised. Set to "*" to require all variables found in the template. |
| exit_conditions | Optional[List[str]] | ["text"] | Defines when the agent stops processing messages. Pass "text" to stop the Agent when it generates a message without tool calls. Pass the name of a tool to stop the Agent after it successfully runs this tool. Multiple exit conditions can be specified, and the Agent stops when any one is met. |
| state_schema | Optional[Dict[str, Any]] | None | Optional schema for managing the runtime state used by tools. It defines extra information—such as documents or context—that tools can read from or write to during execution. You can use this schema to pass parameters that tools can both produce and consume during a call. This means that when a pipeline runs, tools can read from the Agent's state (for example, the current set of retrieved documents) and write into or update this state as they run. |
| max_agent_steps | int | 100 | Maximum number of steps (LLM calls) the Agent runs before stopping. Defaults to 100. If the Agent reaches this limit, it stops execution and returns all messages and state accumulated up to that point. A warning is logged when this limit is reached. Increase this value for complex tasks that require many tool calls. |
| streaming_callback | Optional[StreamingCallbackT] | None | Function invoked for streaming responses. To enable streaming, set streaming_callback to deepset_cloud_custom_nodes.callbacks.streaming.streaming_callback. To learn more about streaming, see Enable Streaming. |
| raise_on_tool_invocation_failure | bool | False | Whether to raise an error when a tool call fails. If set to False, the exception is turned into a chat message and passed to the LLM. |
| tool_invoker_kwargs | Optional[Dict[str, Any]] | None | Additional keyword arguments to pass when invoking a tool. |
Run Method Parameters
These are the parameters you can configure for the component's run() method. This means you can pass these parameters at query time through the API, in Playground, or when running a job. For details, see Modify Pipeline Parameters at Query Time.
| Parameter | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| messages | List[ChatMessage] | List of Haystack ChatMessage objects to process. If a list of dictionaries is provided, each dictionary will be converted to a ChatMessage object. | |
| streaming_callback | Optional[StreamingCallbackT] | None | A function to handle streamed responses. You can configure the same callback function to emit tool results when a tool is called. |
| system_prompt | Optional[str] | None | System prompt for this specific run. If provided, it overrides the default system prompt configured during initialization. This allows you to dynamically adjust the Agent's behavior for different queries. |
| user_prompt | Optional[str] | None | User prompt for this specific run. If provided, it overrides the default user_prompt configured during initialization. The rendered prompt is appended to the provided messages. |
| generation_kwargs | Optional[Dict[str, Any]] | None | Additional keyword arguments for the LLM. These parameters override the parameters passed during component initialization, allowing fine-grained control over chat generation at runtime. |
| tools | Optional[Union[List[Tool], Toolset, List[str]]] | None | Optional list of Tool objects, a Toolset, or list of tool names to use for this run. When passing tool names, tools are selected from the Agent's originally configured tools. This allows you to dynamically select which tools the Agent uses at query time. |
| break_point | Optional[AgentBreakpoint] | None | An AgentBreakpoint, can be a Breakpoint for the "chat_generator" or a ToolBreakpoint for "tool_invoker". Used for debugging and monitoring agent execution. |
| snapshot | Optional[AgentSnapshot] | None | A dictionary containing a snapshot of a previously saved agent execution. The snapshot contains the relevant information to restart the Agent execution from where it left off. |
| kwargs | Any | Additional parameters to pass to the Agent's state_schema. The keys must match the schema defined in the Agent's state_schema. |
Was this page helpful?