Configure an Agent: Model, System Prompt, and Tools
Choose the Agent's model and tools and learn how the Agent component works.
About This Task
You can add MCP servers, pipelines, and custom code as tools. Make sure the tool's name and description are meaningful and help the Agent decide when to use the tool. Add instructions on how to use the tool in the Agent's prompt.
Prerequisites
- For an explanation of the Agent, its tools and memory, see AI Agent and Agent Tools.
- For the
Agentcomponent reference and parameter documentation, see Agent. - Make sure Haystack Platform is connected to the provider of the model you want to use. The Agent works with chat models that support tool calls. For details on how to connect, see Using Hosted Models and External Services.
- For instructions on how to write prompts, see Writing Prompts in Haystack Platform.
- Understanding of pipelines and components in Haystack Platform. For details, see Pipelines and Pipeline Components.
Configure the Agent
Configure the Model and System Prompt
- Drag the Agent component onto the canvas from the Component Library.
- Click the
Modelfield to open the Agent configuration panel, and choose the model from the list. - Enter the system prompt for the Agent.
Add an MCP Server as a Tool
The server must be a remote server. To use a local server, first deploy it to a remote server.
- In the Tools section of the Agent configuration panel, click Add Tool.
- Choose MCP Server.
- Choose the transport protocol supported by the MCP Server you want to connect to. You'll find this information in the MCP Server documentation.
- Choose Server-Sent Events (SSE) to keep an open connection and receive real-time updates as they occur.
- Choose Streamable HTTP to receive updates in chunks as they become available.
- Give your server a name to help you identify it later.
- Enter the server URL.
- Optionally, enter an authentication token if the server requires one.
MCP API Key
If you enter the MCP API key when adding the tool, it's automatically added as a workspace secret with the MCP server name.
- Click Connect. The MCP server details open.
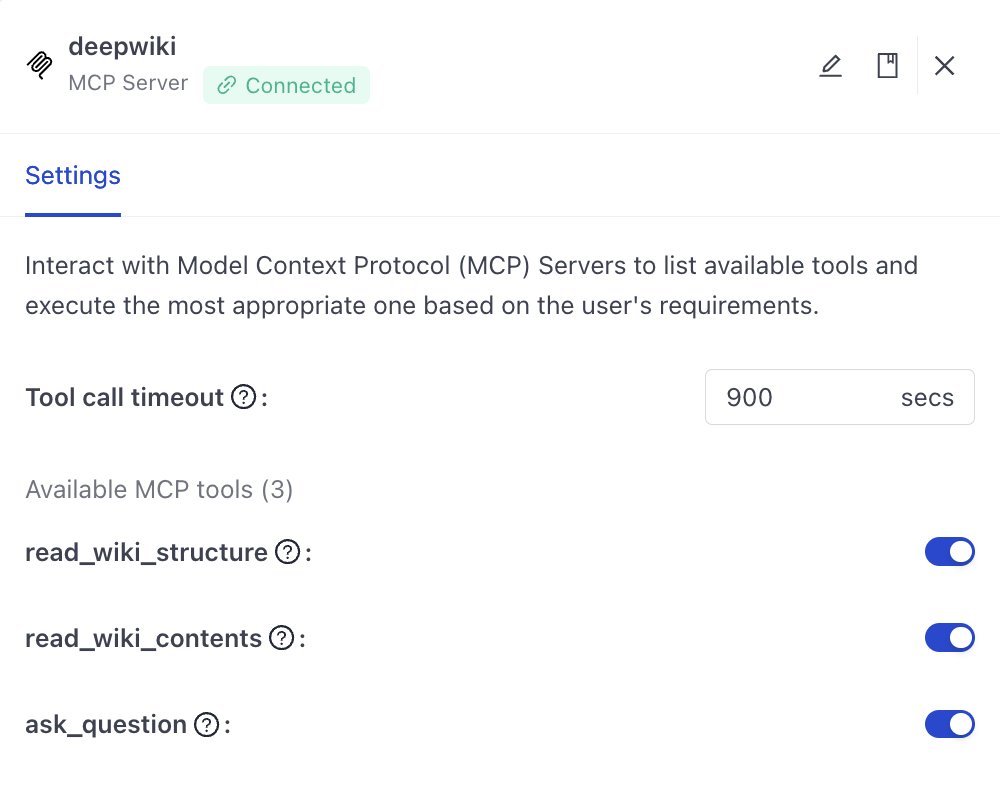
- Set the tool call timeout. This is the maximum time in seconds the Agent will wait for a response from the MCP server.
- From the list of available MCP tools, choose the tools you want to expose to the Agent.
You can run MCP tools on their own from the agent component card. Click Manage Tool next to the MCP server and choose the tool to run. Use this to debug or test tools without running the whole agent. For details, see Run Components and Pipelines in Builder
Example Configuration
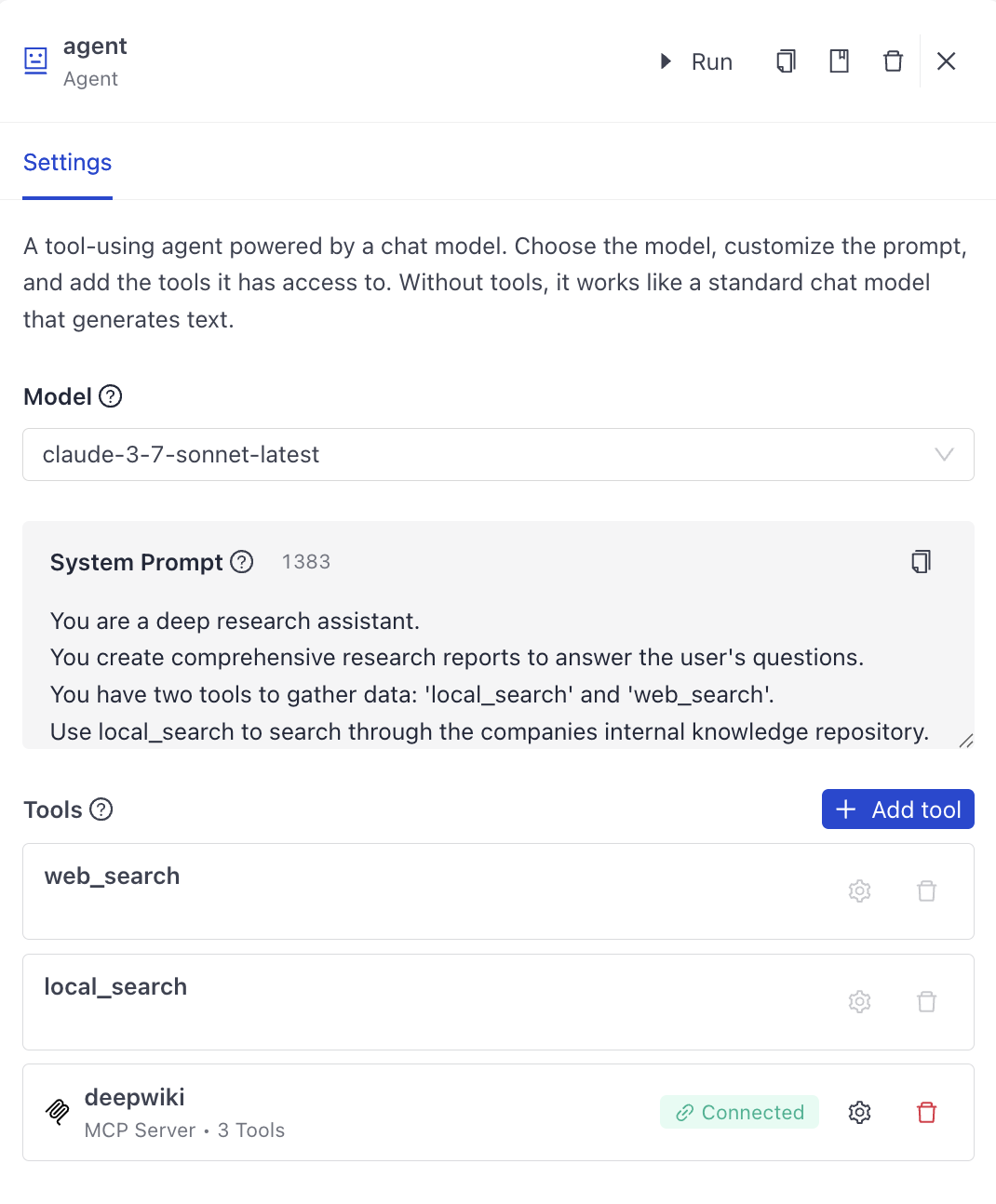
Add Custom Code as a Tool
You can add custom Python functions as tools to your Agent. The code must use the @tool decorator that automatically converts your function into a tool. Each tool must have a name, description, and parameters.
For detailed explanation of custom code as tools, see Agent Tools.
- In the Tools section of the Agent configuration panel, click Add Tool.
- Choose Code as the tool type.
- Enter the Python code for your tool function. The code must use the
@tooldecorator and must define a function that the Agent can call. Use Python'styping.Annotatedto add descriptions to parameters. This helps the Agent understand what each parameter does. You can use the example code as a starting point. Your code is immediately validated so you can easily debug it before deploying the Agent.
You can also use the AI assistant to generate code for your custom tool. To do this, click the AI Assistant button on the tool card, write your request in the prompt, and watch how the code gets generated.
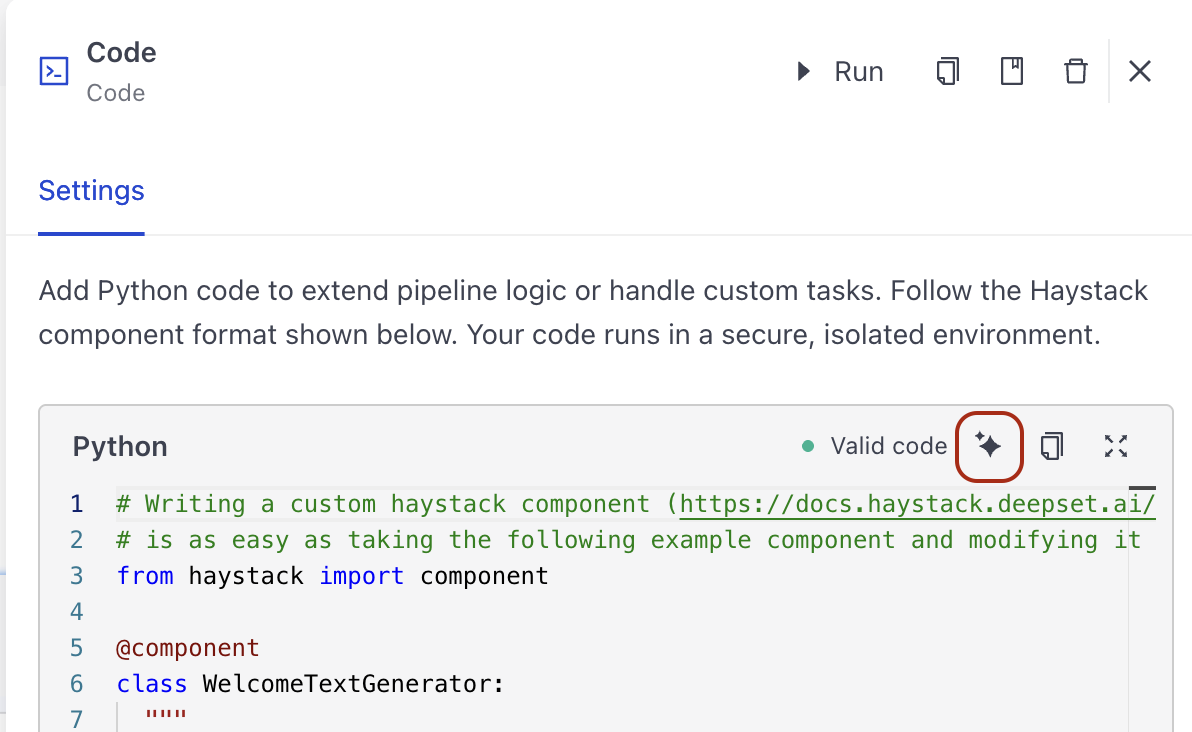
- Add a tool name and description. Make sure the name is unique and descriptive. Make sure the description clearly explains what the tool does. The Agent uses the tool's name and description to decide when to use it.
You can run your custom tools on their own from the agent component card. Click Manage Tool next to the tool and choose the tool to run.
Add a Pipeline as a Tool
You can add an existing pipeline or create one from a template. Such pipeline becomes detached from the original pipeline, so any changes you make to the original pipeline don't affect the tool pipeline. You can edit the pipeline tool directly from the Agent component card.
- In the Tools section of the Agent configuration panel, click Add Tool.
- Choose Pipeline as the tool type.
- In the Create Pipeline Tool window:
- Choose if you want to start from an existing pipeline or from a template.
- If you're starting from an existing pipeline, choose a pipeline from the list, and then choose the version you want to use.
- If you're starting from a template, choose the template to use.
- Enter a name and a description for the pipeline tool. Make sure they're meaningful as the agent uses them to decide when to use the tool.
- Click Add Pipeline Tool. The Agent configuration panel opens.
- Under Tools, click the Manage Tool icon next to the pipeline you just added.
- Choose the pipeline inputs and outputs you want to expose to the Agent:
- Expand Pipeline Inputs.
- Choose how you want the pipeline to receive its inputs:
- Choose LLM for the agent to automatically generate the input and feed it to the pipeline.
- Choose State to read the input from the agent's state. Input stored in state is the input that earlier components or tools generated.
- Expand Pipeline Outputs and choose how to handle the pipeline's outputs:
- Choose LLM to feed the pipeline output to the agent. This is useful if the agent needs to use the pipeline output in its next turn.
- Choose State to store the pipeline output in the agent's state. This is useful if you want the output to be available to other tools or components in the pipeline.
- Choose Both to store the output in both the agent's state and feed it to the agent.
You can run pipeline tools on their own from the agent component card. Click Manage Tool next to the pipeline tool and then choose Run.
Use this to debug or test tools without running the whole agent. For details, see Run Components and Pipelines in Builder.
Was this page helpful?