Pipelines
Pipelines are powerful and highly flexible systems that form the engine for your app. They consist of components that process your data and perform various tasks on it. Each component in a pipeline passes its output to the next component as input.
How Do Pipelines Work?
Pipelines are composed of connected components. Each component processes a piece of your data, such as documents, and performs specific tasks before passing the output to the next component. For example, a basic RAG pipeline may include:
- A
TextEmbedderthat takes the user query and turns it into a vector. - A
Retrieverthat receives the vector from theTextEmbedderand uses it to fetch relevant documents from the document store. - A
PromptBuilderthat injects the user query and the documents from theRetrieverinto the prompt. - A
Generatorthat uses the prompt from thePromptBuilder, including the documents, to generate the response.
Components function like modular building blocks that you can mix, match, and replace to form various pipeline configurations, such as loops, branches, or simultaneous flows. When connecting the components, it's crucial to ensure the output type of one component matches the input type of the next. Each component receives only the data it needs, which speeds up the pipeline and makes it easier to debug.
For component compatibility, check individual pages under Pipeline Components. When building in Pipeline Builder, you can check compatible connections if you hover your mouse over the connection point of a component.
Haystack Enterprise Platform uses Haystack pipelines, which means pipelines accept Haystack objects as input and output. For more information, see Haystack documentation.
Connection Types
Pipelines in Haystack Enterprise Platform are flexible and multifunctional. While you can still create simple pipelines performing one function, like answering queries, you can also use them to build complex workflows.
Connection Validation
When you connect components in a pipeline, it validates that their outputs and inputs match and are explicitly indicated and, if needed, produces detailed errors.
Branches
Pipelines can branch to process data simultaneously. For example, each pipeline branch can have a different converter, each dedicated to a specific file type, allowing for efficient parallel processing.
Loops
In loops, components operate iteratively, with a set limit on repetitions. This is useful in scenarios such as self-correcting loops, where a validator component checks the generator's output and potentially cycles it back for correction until it meets the quality standard and can be sent further down the pipeline.
How Do Pipelines Use Your Files?
Pipelines run on the documents produced by the indexes they're connected to. An index preprocesses the files from a Haystack Platform workspace, converts them into documents, and writes them into a document store where a pipeline can access them. A single pipeline can be connected to multiple indexes. For details, see Indexes.
One file may produce multiple documents. Documents inherit metadata from files. Your indexing pipeline defines the exact steps for preprocessing the files.
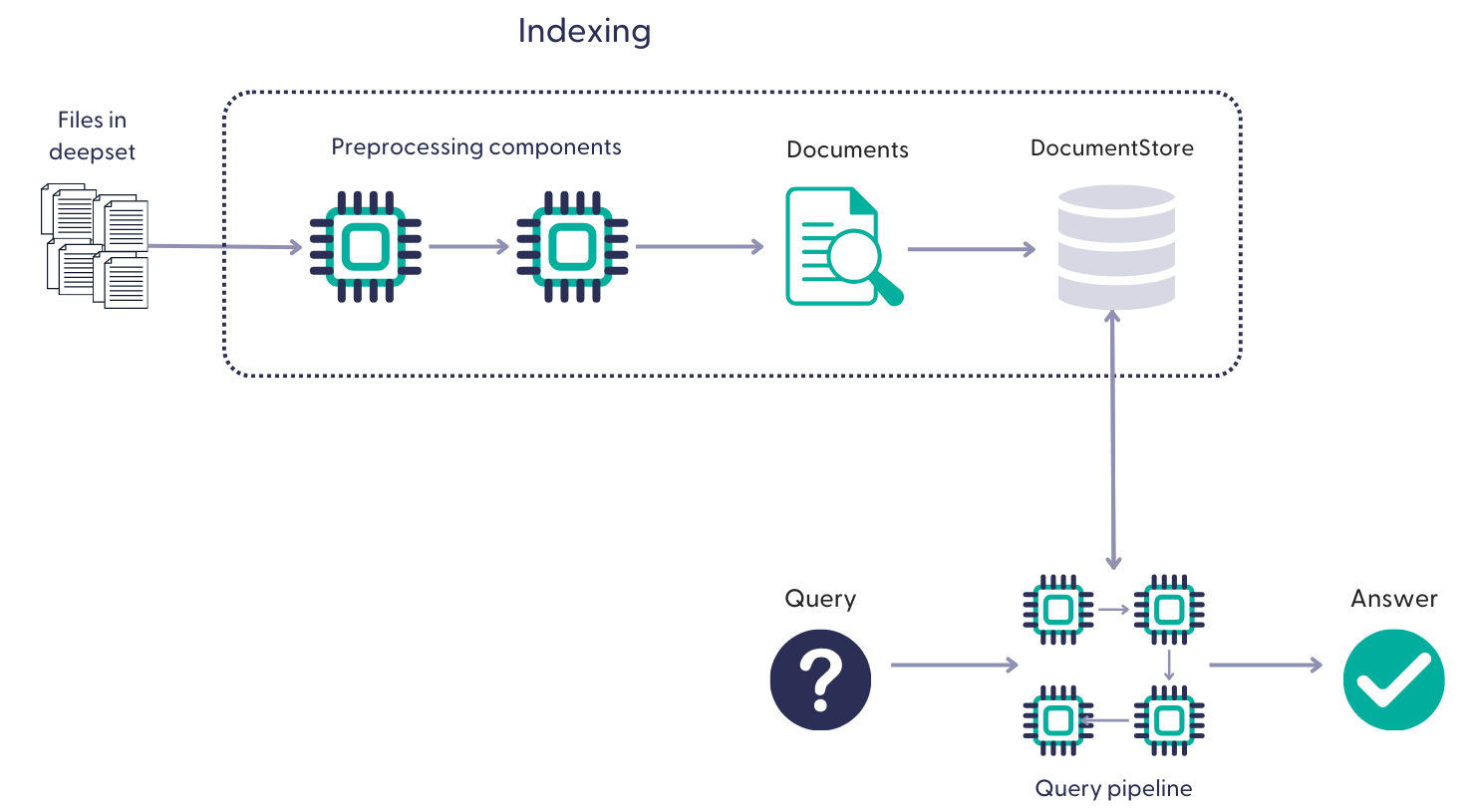
Building Pipelines
Pipelines contain recipes for how to execute a query. A typical pipeline that runs on your files in Haystack Platform, receives the user query, retrieves the relevant documents, and processes them through the components to arrive at an answer.
Example of a pipeline
components:
bm25_retriever: # Selects the most similar documents from the document store
type: haystack_integrations.components.retrievers.opensearch.bm25_retriever.OpenSearchBM25Retriever
init_parameters:
document_store:
init_parameters:
use_ssl: True
verify_certs: False
hosts:
- ${OPENSEARCH_HOST}
http_auth:
- "${OPENSEARCH_USER}"
- "${OPENSEARCH_PASSWORD}"
type: haystack_integrations.document_stores.opensearch.document_store.OpenSearchDocumentStore
top_k: 20 # The number of results to return
query_embedder:
type: haystack.components.embedders.sentence_transformers_text_embedder.SentenceTransformersTextEmbedder
init_parameters:
model: "intfloat/e5-base-v2"
device: null
embedding_retriever: # Selects the most similar documents from the document store
type: haystack_integrations.components.retrievers.opensearch.embedding_retriever.OpenSearchEmbeddingRetriever
init_parameters:
document_store:
init_parameters:
use_ssl: True
verify_certs: False
http_auth:
- "${OPENSEARCH_USER}"
- "${OPENSEARCH_PASSWORD}"
type: haystack_integrations.document_stores.opensearch.document_store.OpenSearchDocumentStore
top_k: 20 # The number of results to return
document_joiner:
type: haystack.components.joiners.document_joiner.DocumentJoiner
init_parameters:
join_mode: concatenate
ranker:
type: haystack.components.rankers.transformers_similarity.TransformersSimilarityRanker
init_parameters:
model: "intfloat/simlm-msmarco-reranker"
top_k: 8
device: null
model_kwargs:
torch_dtype: "torch.float16"
prompt_builder:
type: haystack.components.builders.prompt_builder.PromptBuilder
init_parameters:
template: |-
You are a technical expert.
You answer questions truthfully based on provided documents.
Ignore typing errors in the question.
For each document check whether it is related to the question.
Only use documents that are related to the question to answer it.
Ignore documents that are not related to the question.
If the answer exists in several documents, summarize them.
Only answer based on the documents provided. Don't make things up.
Don't reference documents.
Just output the structured, informative and precise answer and nothing else.
If the documents can't answer the question, say so.
These are the documents:
{% for document in documents %}
Document[{{ loop.index }}]:
{{ document.content }}
{% endfor %}
Question: {{question}}
Answer:
llm:
type: haystack.components.generators.openai.OpenAIGenerator
init_parameters:
api_key: {"type": "env_var", "env_vars": ["OPENAI_API_KEY"], "strict": False}
model: "gpt-4o"
generation_kwargs:
max_tokens: 400
temperature: 0.0
seed: 0
answer_builder:
init_parameters: {}
type: haystack.components.builders.answer_builder.AnswerBuilder
connections: # Defines how the components are connected
- sender: bm25_retriever.documents
receiver: document_joiner.documents
- sender: query_embedder.embedding
receiver: embedding_retriever.query_embedding
- sender: embedding_retriever.documents
receiver: document_joiner.documents
- sender: document_joiner.documents
receiver: ranker.documents
- sender: ranker.documents
receiver: prompt_builder.documents
- sender: ranker.documents
receiver: answer_builder.documents
- sender: prompt_builder.prompt
receiver: llm.prompt
- sender: llm.replies
receiver: answer_builder.replies
max_loops_allowed: 100
inputs: # Define the inputs for your pipeline
query: # These components will receive the query as input
- "bm25_retriever.query"
- "query_embedder.text"
- "ranker.query"
- "prompt_builder.question"
- "answer_builder.query"
filters: # These components will receive a potential query filter as input
- "bm25_retriever.filters"
- "embedding_retriever.filters"
outputs: # Defines the output of your pipeline
documents: "ranker.documents" # The output of the pipeline is the retrieved documents
answers: "answer_builder.answers" # The output of the pipeline is the generated answer
Inputs
Pipelines always take Input as the first component. When working in Builder, drag Input from the Inputs group onto the canvas and then connect it to the components that should receive its outputs.
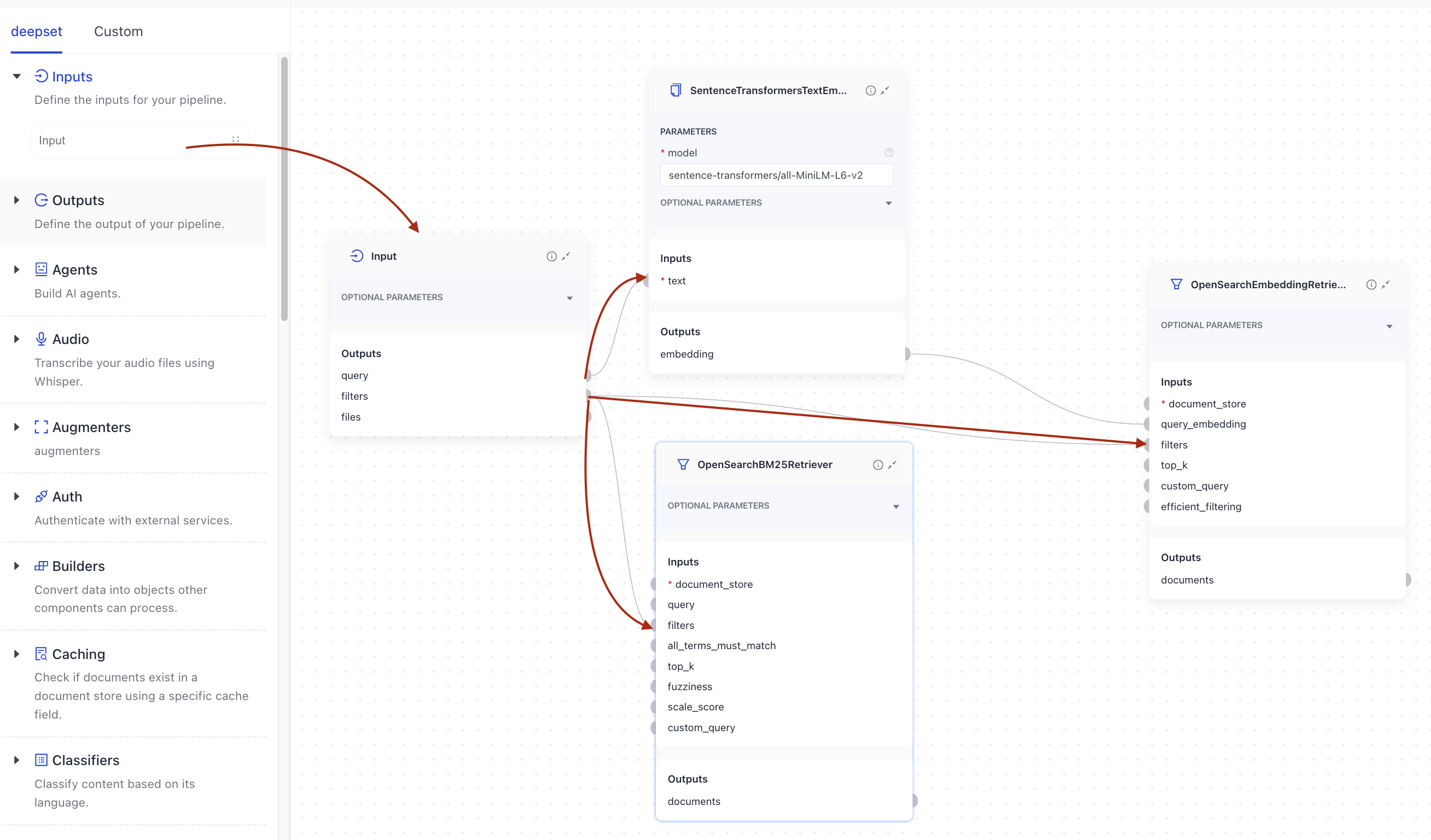
When working in YAML editor, you must explicitly specify the inputs and the components that receive them:
inputs: # Define the inputs for your pipeline
query: # These components will receive the query as input
- "bm25_retriever.query"
- "query_embedder.text"
- "ranker.query"
- "prompt_builder.question"
- "answer_builder.query"
filters: # These components will receive a potential query filter as input
- "bm25_retriever.filters"
- "embedding_retriever.filters"
Filters are documents' metadata keys by default. This means that if your documents have the following metadata: {"category": "news"}, when searching in Playground, users can narrow down the search to the documents matching this category. You can also pass filters at search time with the Search endpoint. For more information about filters, see Working with Metadata.
Outputs
The output of pipelines matches the output of the last component. However, it must be one of the following data classes:
- List of
Documentobjects (usually document search pipelines) - List of
Answerobjects, including the following subclasses:- List of
ExtractedAnswerobjects (usually extractive question answering pipelines) - List of
GeneratedAnswerobjects (usually RAG pipelines or pipelines that use large language models to generate answers)
- List of
The output can be a list of documents, a list of answers, or both. Ensure the last component in your pipeline produces one or both of these outputs. For example, you may need to add an AnswerBuilder after a Generator to produce a list of GeneratedAnswerobjects. For more information, see Pipeline Components. To learn more about data classes, see Haystack data classes.
In Pipeline Builder, to finalize the pipeline with the correct output, drag the Output component onto the canvas and connect it to the components that produce the documents or answers you want to include:
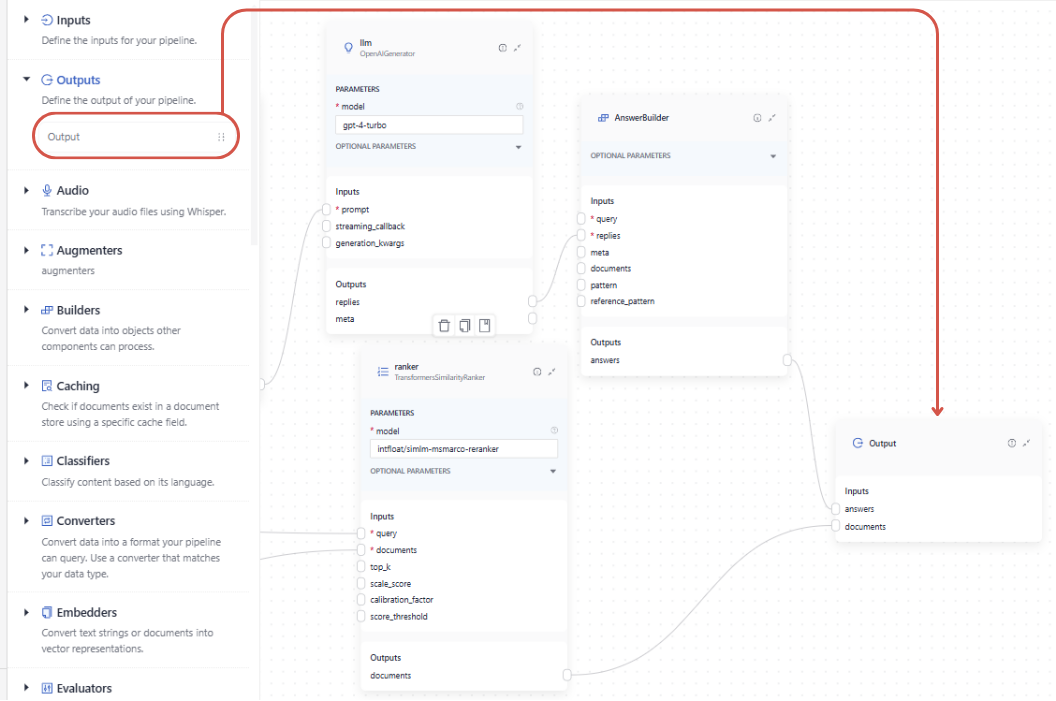
When working in the YAML editor, you must explicitly specify the outputs and the components that provide them:
outputs: # Defines the output of your pipeline
documents: "ranker.documents" # The output of the pipeline is the retrieved documents
answers: "answer_builder.answers" # The output of the pipeline is the generated answers
Pipeline Service Levels
To save costs and meet your infrastructure and service requirements, your pipelines are assigned service levels. There are three service levels available:
- Draft: This is a service level automatically assigned to new and undeployed pipelines, so that you can easily distinguish them from the deployed ones.
- Development: Pipelines at this level are designed for testing and running experiments. They have no replicas by default, and their time to standby is short, so they can save resources whenever these pipelines aren't used. When you deploy a draft pipeline, it becomes a development pipeline.
- Production: This level is recommended for business-critical scenarios where you need the pipeline to be scalable and reliable. Pipelines at this level include one replica by default and a longer time-to-standby period than other service levels. With heavy traffic, the number of replicas grows up to 10.
This table gives an overview of the default settings that come with each service level:
| Service level | Description | Idle Timeout | Scaling (replicas) | How to enable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Production | Designed for critical business scenarios that require reliable and scalable pipelines. | 24 hours | 1 at all times, scales up to 10 if traffic is heavy | - In Haystack Enterprise Platform, on the Pipelines page - Through the Update Pipeline REST API endpoint |
| Development | Designed for testing and experimenting purposes. | 20 minutes | 0 | - By switching off the Production service level for a deployed production pipeline in Haystack Enterprise Platform - Through the Update Pipeline REST API endpoint- By deploying a draft pipeline |
| Draft | Indicates an undeployed pipeline. | n/a | 0 | - By undeploying a production or development pipeline - All new pipelines are automatically classified as drafts |
Idle timeout is the time after which an unused pipeline enters a standby mode to save resources. Inactive pipelines don't use up the pipeline hours included in your plan. You can customize the idle timeout for each pipeline in the pipeline's Settings tab or through the Update Pipeline REST API endpoint. The maximum idle timeout is 30 days.
To use a pipeline on standby, activate it either on the Pipelines page or by initiating a search using that pipeline.
Replicas are the number of duplicate versions of a pipeline that are available. In case there is a spike in demand, Haystack Platform seamlessly switches to a functioning replica to maintain uninterrupted service. You can configure the minimum and maximum number of replicas in the pipeline's Settings tab or through the Update Pipeline REST API endpoint. The maximum number of replicas is 10.
You can change the service level of your pipeline at any time. For details, see Change the Pipeline's Service Level.
The Pipelines Page
All the pipelines created by your organization are listed on the Pipelines page. The pipelines listed under Deployed are the ones that you can run your search with. The pipelines under In Development are drafts you must deploy before you can use them for your search.
The Pipeline Details Page
Clicking a pipeline name opens Pipeline Details, where you can check all the information about your pipeline, including pipeline logs and search history. You can check the following information about the pipeline:
- ID
- Status
- Service level
- Pipeline overview
- Search history
- Logs
- Settings
Pipeline Status
Draft pipelines are not deployed. When you deploy a pipeline, it changes its status as follows:
- Deploying: The pipeline is being deployed.
- Deployed: The pipeline is ready to resolve queries.
- Failed to deploy: It's a fatal state. Your pipeline was not deployed and you can't search with it. For ideas on how to fix it, see Troubleshoot Pipeline Deployment.
Overview
The overview shows the feedback you received for your pipeline and its latency.
Search history
The Search History tab shows the queries run with this pipeline and their results. You can customize the Search History table columns to show the information you need. You can also export the entire search history as a CSV file for a specific time period. This is useful for analyzing the performance of your pipeline over time.
Logs
Use the logs to troubleshoot issues with your pipeline. You can filter the logs by message and pipeline type or date added. You can also search for keywords in log messages.
Settings
GPU Acceleration
Pipelines use CPU by default. Turn on GPU support on the Settings tab when your pipeline includes components that run better on a GPU, such as DoclingConverter, SentenceTransformersDocumentEmbedder, or custom components that use AI models.
When GPU support is on, the pipeline checks whether a component needs a GPU and assigns one automatically. GPUs are only used when required and are not reserved for the entire pipeline run.
If GPU support is off and your pipeline includes components that rely on a GPU, those components run on the CPU instead. This can slow down processing and may cause timeouts, especially for larger or more complex pipelines.
For detailed instructions, see Enable GPU Acceleration.
Pipeline Scaling
To increase availability, set the number of replicas allocated to a pipeline. Haystack Platform automatically scales replicas up or down based on traffic, and depending on the maximum and minimum number of replicas you set.
For production pipelines, set at least two replicas. This setup helps keep your pipeline available if one replica fails.
Adding more replicas can increase your costs.
Idle Timeout
Set the idle timeout to define how long a pipeline can remain inactive before it enters standby mode. When a pipeline becomes idle, Haystack Platform scales its replicas down to zero.
Idle pipelines do not consume the pipeline hours included in your plan. For example, if you set the idle timeout to 12 hours, the pipeline enters standby mode after 12 hours of inactivity.
This setting is useful for saving costs when you don't need your pipeline to be always available.
Was this page helpful?