Document Stores
Document store is a database that stores the pre-processed documents resulting from your indexing pipeline. The query pipeline uses retrievers to access the document store and fetch relevant documents to resolve queries.
The Document Store Concept
A document store is a Haystack concept that refers to an object that stores your data. It's an interface to a database like OpenSearch, Weaviate, or Pinecone, for storing and retrieving your data.
Document store stores data as Document objects. Each document has a unique ID, metadata, and can optionally include vector representations (embeddings) for enhanced search capabilities.
In Haystack Enterprise Platform, a document store is a parameter of other components, such as a Retriever or DocumentWriter. To make things easier, document stores appear as component cards in Pipeline Builder.
Document
To store your data in a document store, you must convert them into Document objects first. Documents are individual pieces of information that can include text, data frames, or binary data. When an indexing pipeline runs, files uploaded to your Haystack Platform workspace are preprocessed, cleaned, split, and converted into Document objects using PreProcessor components. One file can be split into multiple documents. Once processed, the DocumentWriter component writes them into a document store.
Query pipelines work on the documents stored in the document store, not directly on the uploaded files. A Retriever fetches the relevant documents from the document store and passes them to subsequent components in the pipeline to resolve queries or run other tasks.
Document is a Haystack data class with specific properties you can access. One file may produce multiple documents. Documents inherit metadata from files. For details, see Haystack documentation for data classes.
Indexes and Document Store
In Haystack Platform, when building an index, you specify the document store where it writes the data. The index then becomes a parameter of this document store. When configuring the document store, you can choose the index to use from the document store card.
Writing Documents into the Document Store
Index defines how and where you write the resulting document. You can write documents into a document store using DocumentWriter. As a best practice, include DocumentWriter as the last component in your index, and make sure it's connected to a document store.
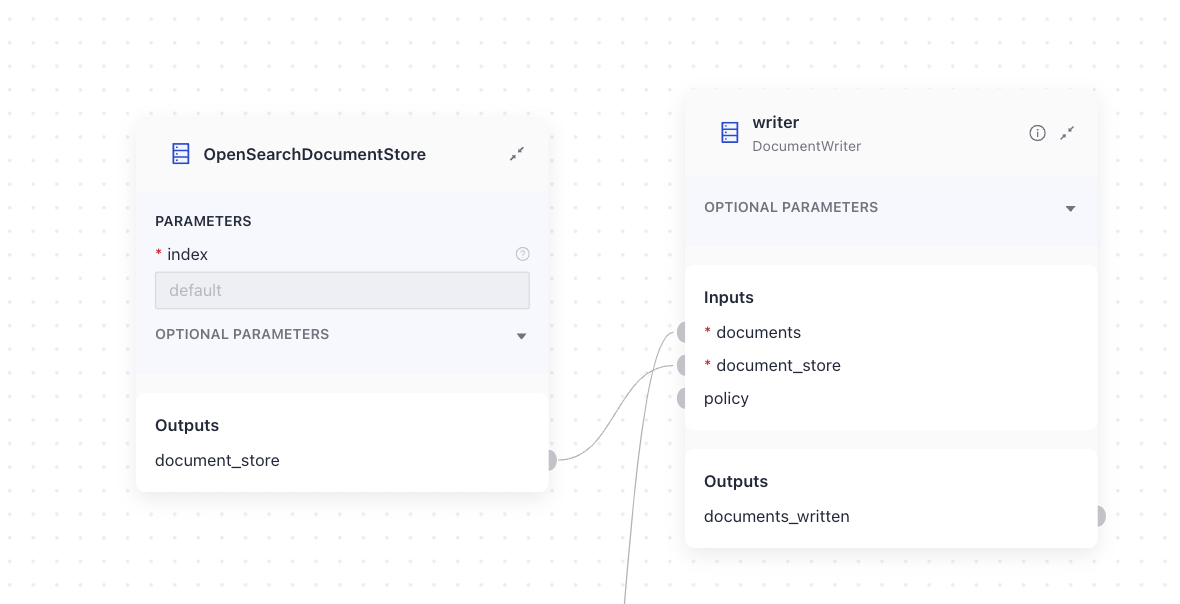
Retrieving Documents
Document stores work with retrievers. Retrievers in your query pipeline access the document store to fetch the documents relevant to the query. Each document store has dedicated retrievers, usually a keyword retriever, a vector retriever, and sometimes a hybrid retriever that combines both. This is because retrievers rely on the document store technology to fetch documents.
Connect a Retriever to a matching document store to enable it to fetch documents from this document store.
Configuring a Document Store
In Pipeline Builder
Drag a document store from the Component Library connect it to DocumentWriter or a Retriever. You can configure the document store parameters on the document store card. For detailed parameter explanation, see Haystack's Integrations API documentation.
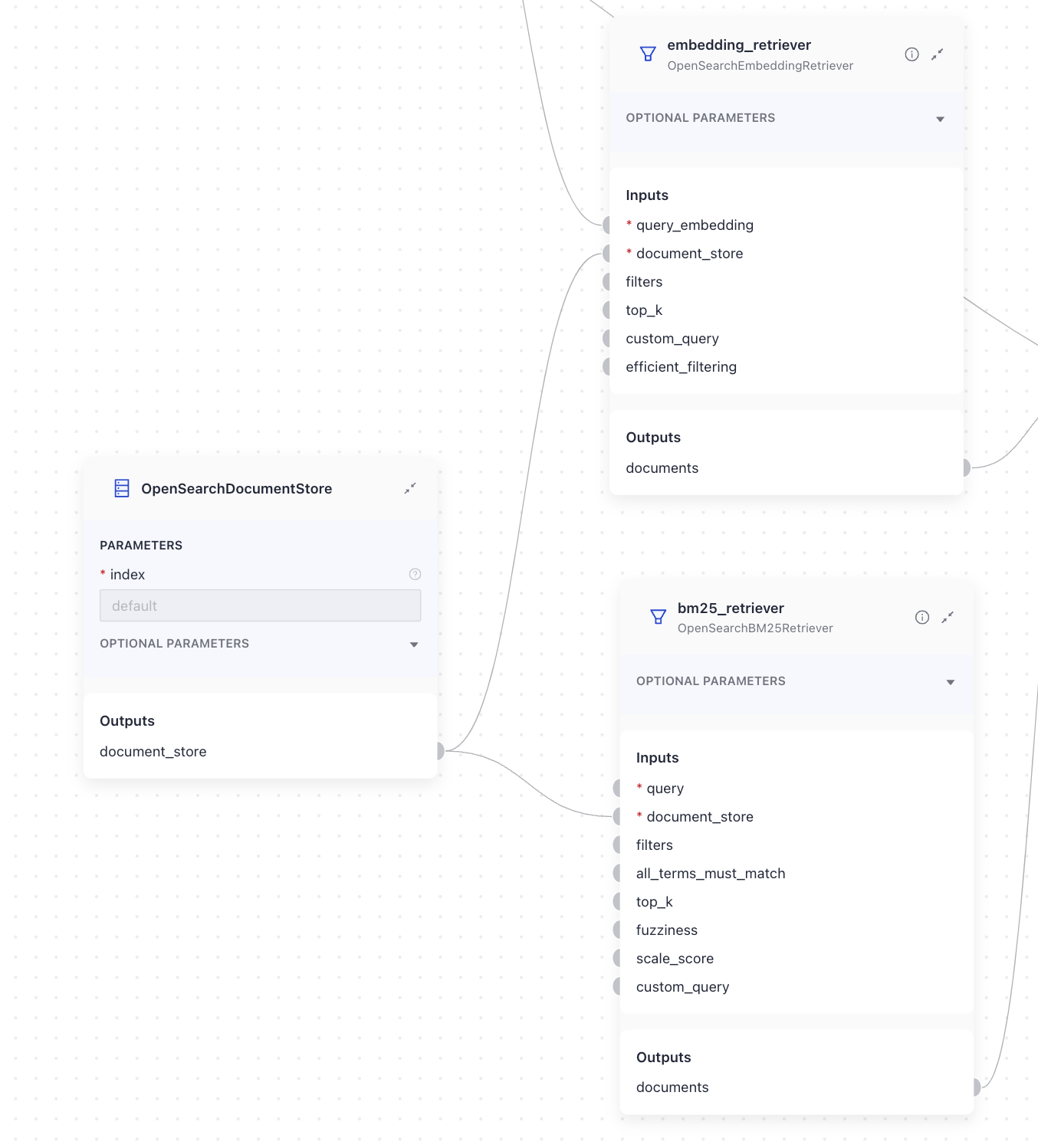
If multiple components in a pipeline need a document store and use the same configuration, you only need to add one document store card. You can then connect this single card to all the components that use it. But if different components require different document store configurations, add a separate document store card for each unique setup. Then, configure each card as needed and connect them to the right components:

In YAML
Pass the document store configuration in the document_store parameter of DocumentWriter or a Retriever:
bm25_retriever: # Selects the most similar documents from the document store
type: haystack_integrations.components.retrievers.opensearch.bm25_retriever.OpenSearchBM25Retriever
init_parameters:
document_store: #this is the document store configuration
type: haystack_integrations.document_stores.opensearch.document_store.OpenSearchDocumentStore
init_parameters:
hosts:
index: default
max_chunk_bytes: 104857600
embedding_dim: 768
return_embedding: false
method:
mappings:
settings:
create_index: true
http_auth:
use_ssl:
verify_certs:
timeout: 10
top_k: 20 # The number of results to return
fuzziness: 0
Supported Document Stores
Core Document Stores
OpenSearch is the only core document store of Haystack Enterprise Platform. We manage its infrastructure and credentials and have access to its index and indexing information, such as the detailed status of files being indexed. Haystack Platform also manages file updates, including the metadata and deletions, and keeps the document store in sync.
Integrations
These document stores run on your infrastructure, and you're responsible for managing the credentials (you provide them in the configuration). When you deploy your indexing pipeline, Haystack Platform creates the index for these document stores, but the number of indexed files will always display as 0.
For integrations, Haystack Enterprise Platform also handles metadata updates and file deletions, ensuring that changes are reflected in the document store.
Other
Snowflake. Snowflake is a table database that doesn't have an index. You can query your Snowflake data using SnowflakeTableRetriever, which accesses the database and fetches a table that matches the SQL query.
Comparison
This table compares the document stores in Haystack Enterprise Platform:
| Document store | Infrastructure | Index | Indexing status | File updates (deleting, metadata updates) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenSearch | Managed by Haystack Platform | Managed by Haystack Platform | Shown in details (indexed, skipped, and failed files) | Managed by Haystack Platform |
| Elasticsearch | Your own | Created on pipeline deploy Deleted on pipeline undeploy | No information, always shown as 0 | Managed by Haystack Platform |
| MongoDB | Your own | You need to create a vector search index in MongoDB | No information, always shown as 0 | Managed by Haystack Platform |
| Pinecone | Your own (you need to host the database locally) | Created on pipeline deploy Deleted on pipeline undeploy | No information, always shown as 0 | Managed by Haystack Platform |
| Qdrant | Your own | Created on pipeline deploy Deleted on pipeline undeploy | No information, always shown as 0 | Managed by Haystack Platform |
| Snowflake | Your own | Not available (Snowflake doesn't use indexes) | Not available | You're responsible for managing the tables |
| Weaviate | Your own | Created on pipeline deploy Deleted on pipeline undeploy | No information, always shown as 0 | Managed by Haystack Platform |
Choosing the Right Document Store
Have a look at the Haystack Guide to help you choose the document store that will work best for your scenario.
Was this page helpful?