Tutorial: Creating a Custom RegexBooster Component
Write your own component, upload it to Haystack Enterprise Platform, and use it in your pipelines. In this tutorial, you'll create a RegexBooster component that adjusts document scores based on regex patterns. You'll then learn how to add it to your pipelines.
- Level: Intermediate
- Time to complete: 20 minutes
- Prerequisites:
- Good knowledge of Python.
- Basic knowledge of regular expressions.
- Understanding of how components and pipelines work. Read the following resources:
- A GitHub account and basic knowledge of working with GitHub repositories.
- Haystack Platform API key. For instructions, see Generate an API Key
- Goal: After completing this tutorial, you'll have created a custom component that boosts document scores based on regex patterns. You'll then have uploaded this component to your Haystack Platform workspace and added it to a pipeline.
Prepare the Custom Components Template
You'll create the component using a template we provide. First, we need to prepare it.
- Fork the dc-custom-component-template GitHub repository.
- Clone the forked repository to your local machine.
- Navigate to the
./dc-custom-component-template/src/dc_custom_component/example_components/directory. - Delete the
preprocessorsfolder. - Rename the
example_componentsfolder tocustom_componentsand open it.
The forked repo should now have the following structure:./dc-custom-component-template/src/dc_custom_component/custom_components/rankers/. - Open the
rankersfolder and rename thekeyword_booster.pyfile toregex_booster.py.
Result: Your template now has the following structure:
dc-custom-component-template/
├── src/
│ └── dc_custom_component/
│ ├── __about__.py
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── custom_components/
│ └── rankers/
│ └── regex_booster.py
├── pyproject.toml
├── README.md
└── tests/
Set Up a Virtual Environment
- Install Hatch by running:
pip install hatch. - In your terminal, navigate to the root directory (
./dc-custom-component-template) of your cloned repository. - Create a virtual environment by running:
hatch shell.
Result: The virtual environment is running.
Implement RegexBooster
-
Open the
./dc-custom-component-template/src/dc_custom_component/custom_components/rankers/regex_booster.pyfile. -
Paste the following code replacing all the file contents, and save the file.
import re
from typing import Dict, List
from haystack import component, Document
@component
class RegexBooster:
r"""
A component for boosting document scores based on regex patterns.
This component adjusts the scores of documents based on whether their content
matches specified regular expression patterns. After adjusting scores, it
sorts the documents in descending order of their new scores.
Note:
- Regex matching is case-insensitive by default.
- Multiple regex patterns can match a single document, in which case
the boosts are multiplied together.
- Documents that don't match any patterns keep their original score.
- The component assumes documents already have a 'score' attribute.
Documents without a score are treated as having a score of 0.
Example:
\```python
booster = RegexBooster({
r"\bpython\b": 1.5, # Boost documents mentioning "python" by 50%
r"machine\s+learning": 1.3, # Boost "machine learning" by 30%
r"\bsql\b": 0.8, # Reduce score for documents mentioning "sql" by 20%
})
\```
In this example, a document containing both "python" and "machine learning"
would have its score multiplied by 1.5 * 1.3 = 1.95, effectively boosting
it by 95%.
"""
def __init__(self, regex_boosts: Dict[str, float]):
self.regex_boosts = {re.compile(k, re.IGNORECASE): v for k, v in regex_boosts.items()}
"""
Initialize the component.
:param regex_boosts: A dictionary where:
- Keys are string representations of regular expression patterns.
- Values are float numbers representing the boost factor.
The boost factor must be greater than 1.0 to increase the score,
or between 0 and 1 to decrease it. A boost of exactly 1.0 will
have no effect.
"""
@component.output_types(documents=List[Document])
def run(self, documents: List[Document]) -> Dict[str, List[Document]]:
"""
Apply regex-based score boosting to the input documents.
:param documents: The list of documents to process.
Returns: A dictionary with a single key 'documents',
containing the list of processed documents, sorted by their new scores.
"""
for regex, boost in self.regex_boosts.items():
for doc in documents:
if doc.score is not None and regex.search(doc.content):
doc.score *= boost
documents = sorted(documents, key=lambda x: x.score or 0, reverse=True)
return {"documents": documents} -
Format your code by running
hatch run code-quality:allfrom the project root directory. -
Update RegexBooster version:
- Open the file
./dc-custom-component-template/src/dc_custom_component/__about__.py.. - Change the version to
__version__ = "1.0.0".
- Open the file
Result: The Python implementation for the RegexBooster component is now in the regex_booster.py file, the code is formatted, and the component version is updated.
Add Tests
-
Open the
./dc-custom-component-template/testsfolder and delete theexample_componentsfolder. -
Create a file called
test_regex_booster.py. -
Paste this code into this file and save it:
import pytest
from typing import List, Dict, Any
from haystack import component, Document, Pipeline
from haystack.components.joiners import DocumentJoiner
from dc_custom_component.custom_components.rankers.regex_booster import RegexBooster
# Unit Tests
def test_regex_booster_initialization():
booster = RegexBooster({"pattern": 1.5})
assert len(booster.regex_boosts) == 1
assert list(booster.regex_boosts.values())[0] == 1.5
def test_regex_booster_case_insensitivity():
booster = RegexBooster({r"\bPython\b": 1.5})
doc = Document(content="python is great", score=1.0)
result = booster.run(documents=[doc])
assert result["documents"][0].score == 1.5
def test_regex_booster_multiple_patterns():
booster = RegexBooster({r"\bPython\b": 1.5, r"\bgreat\b": 1.2})
doc = Document(content="Python is great", score=1.0)
result = booster.run(documents=[doc])
assert result["documents"][0].score == 1.5 * 1.2
def test_regex_booster_no_match():
booster = RegexBooster({r"\bJava\b": 1.5})
doc = Document(content="Python is great", score=1.0)
result = booster.run(documents=[doc])
assert result["documents"][0].score == 1.0
def test_regex_booster_sorting():
booster = RegexBooster({r"\bPython\b": 1.5, r"\bJava\b": 1.2})
docs = [
Document(content="Java is okay", score=1.0),
Document(content="Python is great", score=1.0),
Document(content="C++ is fast", score=1.0)
]
result = booster.run(documents=docs)
assert [doc.content for doc in result["documents"]] == ["Python is great", "Java is okay", "C++ is fast"]
def test_regex_booster_no_score():
booster = RegexBooster({r"\bPython\b": 1.5})
doc = Document(content="Python is great")
result = booster.run(documents=[doc])
assert result["documents"][0].score is None
# Integration Tests
@component
class MockRetriever:
@component.output_types(documents=List[Document])
def run(self, query: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
docs = [
Document(content="Python is a programming language", score=0.9),
Document(content="Java is also a programming language", score=0.7),
Document(content="Machine learning is a subset of AI", score=0.5)
]
return {"documents": docs}
@pytest.fixture
def regex_pipeline():
retriever = MockRetriever()
regex_booster = RegexBooster({r"\bPython\b": 1.5, r"\bAI\b": 1.3})
joiner = DocumentJoiner()
pipeline = Pipeline()
pipeline.add_component("retriever", retriever)
pipeline.add_component("regex_booster", regex_booster)
pipeline.add_component("joiner", joiner)
pipeline.connect("retriever.documents", "regex_booster.documents")
pipeline.connect("regex_booster.documents", "joiner.documents")
return pipeline
def test_regex_booster_in_pipeline(regex_pipeline):
results = regex_pipeline.run(data={"query": "programming languages"})
documents = results["joiner"]["documents"]
assert len(documents) == 3
assert documents[0].content == "Python is a programming language"
assert pytest.approx(documents[0].score, 0.01) == 0.9 * 1.5
assert documents[1].content == "Java is also a programming language"
assert pytest.approx(documents[1].score, 0.01) == 0.7
assert documents[2].content == "Machine learning is a subset of AI"
assert pytest.approx(documents[2].score, 0.01) == 0.5 * 1.3
def test_regex_booster_pipeline_no_matches():
@component
class NoMatchRetriever:
@component.output_types(documents=List[Document])
def run(self, query: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
return {
"documents": [
Document(content="C++ is a compiled language", score=0.8),
Document(content="Ruby is dynamic", score=0.6)
]
}
new_pipeline = Pipeline()
new_pipeline.add_component("retriever", NoMatchRetriever())
new_pipeline.add_component("regex_booster", RegexBooster({r"\bPython\b": 1.5, r"\bAI\b": 1.3}))
new_pipeline.add_component("joiner", DocumentJoiner())
new_pipeline.connect("retriever.documents", "regex_booster.documents")
new_pipeline.connect("regex_booster.documents", "joiner.documents")
results = new_pipeline.run(data={"query": "programming languages"})
documents = results["joiner"]["documents"]
assert len(documents) == 2
assert documents[0].content == "C++ is a compiled language"
assert pytest.approx(documents[0].score, 0.01) == 0.8
assert documents[1].content == "Ruby is dynamic"
assert pytest.approx(documents[1].score, 0.01) == 0.6 -
From the root directory of your project, where the
pyproject.tomlis located, run:hatch run testsIf the tests pass, you can upload your component to Haystack Enterprise Platform.
-
Push your changes to the forked repository.
Import RegexBooster to Haystack Enterprise Platform
We use GitHub Actions to build and push components to Haystack Platform. Create a new release for your forked repository and assign a tag to it to trigger the build and the push jobs:
-
Add the
DEEPSET_CLOUD_API_KEYsecret to your repository. This is your Haystack Platform API key.- In your forked repository, go to Settings > Secrets and variables > Actions.
- Click New repository secret.
- Type
DEEPSET_CLOUD_API_KEYas the secret name and paste the API key in the Secret field. - Click Add secret.
For details on GitHub secrets, see Using secrets in GitHub actions.
-
Make sure your repository has workflows enabled. Go to Actions and click Enable workflows.
-
Create a new release:
-
In the left-hand navigation, find Releases and click Create a new release.
-
Click Choose a tag and type
1.0.0as the tag name. -
Click Create a new tag.
- Click Publish release. This triggers tests and code quality check. If these pass, your component is imported to Haystack Enterprise Platform. You can check the status in the Actions tab of your forked repository.
-
Result: RegexBooster is in Haystack Enterprise Platform, ready to be added to a pipeline.
Add RegexBooster to a Pipeline
Let's quickly create a pipeline. If you have one ready, open it for edition in Pipeline Builder.
-
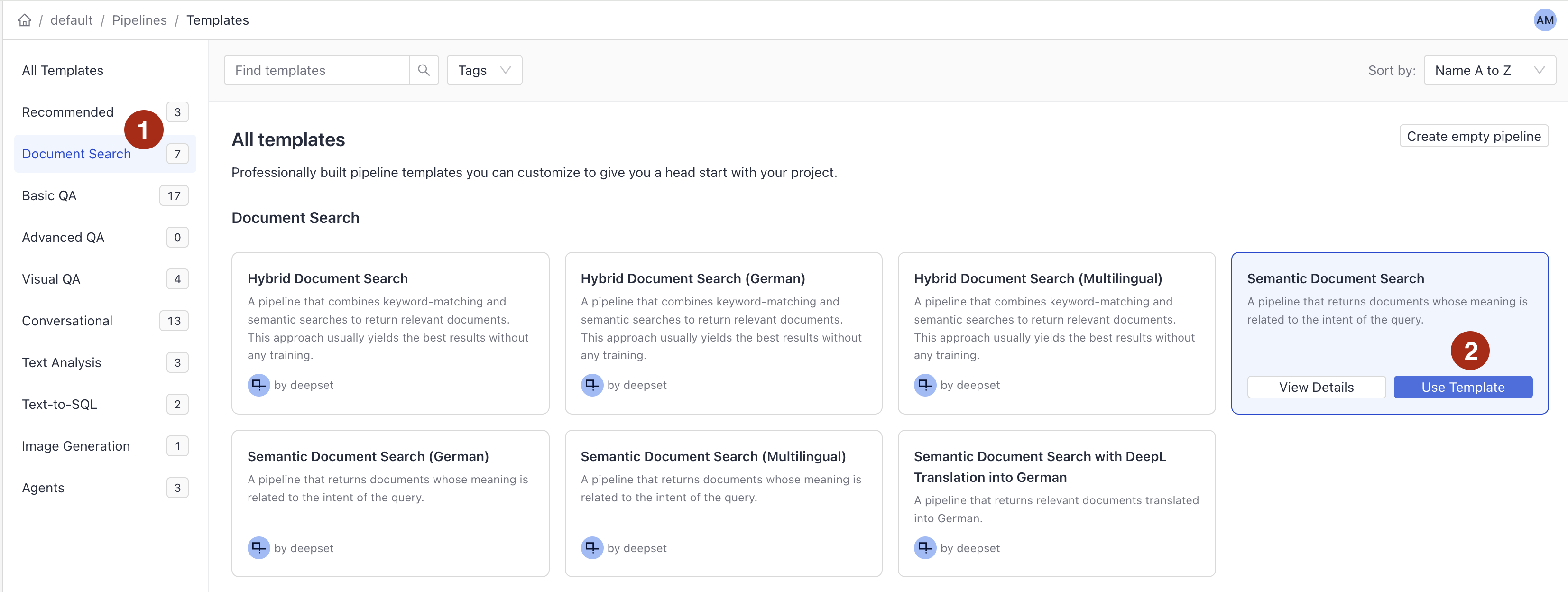
Go to Pipeline Templates.
-
Choose Document Search templates, hover over Semantic Document Search, and click Use template.
-
Click Create a pipeline. You're redirected to Pipeline Builder.
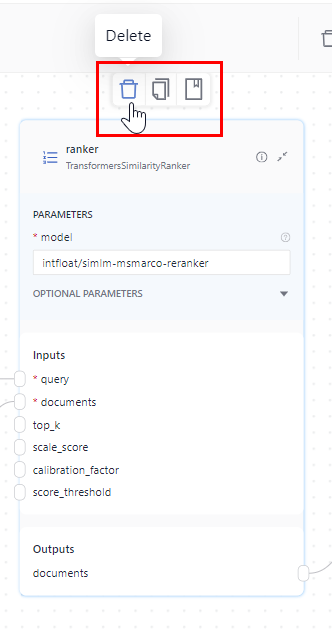
-
Open the Query tab and find the Ranker in your query pipeline components.
-
Click the Ranker card to bring up action icons above it and choose Delete.
-
In the component library, expand Rankers and drag
RegexBoosteronto the canvas.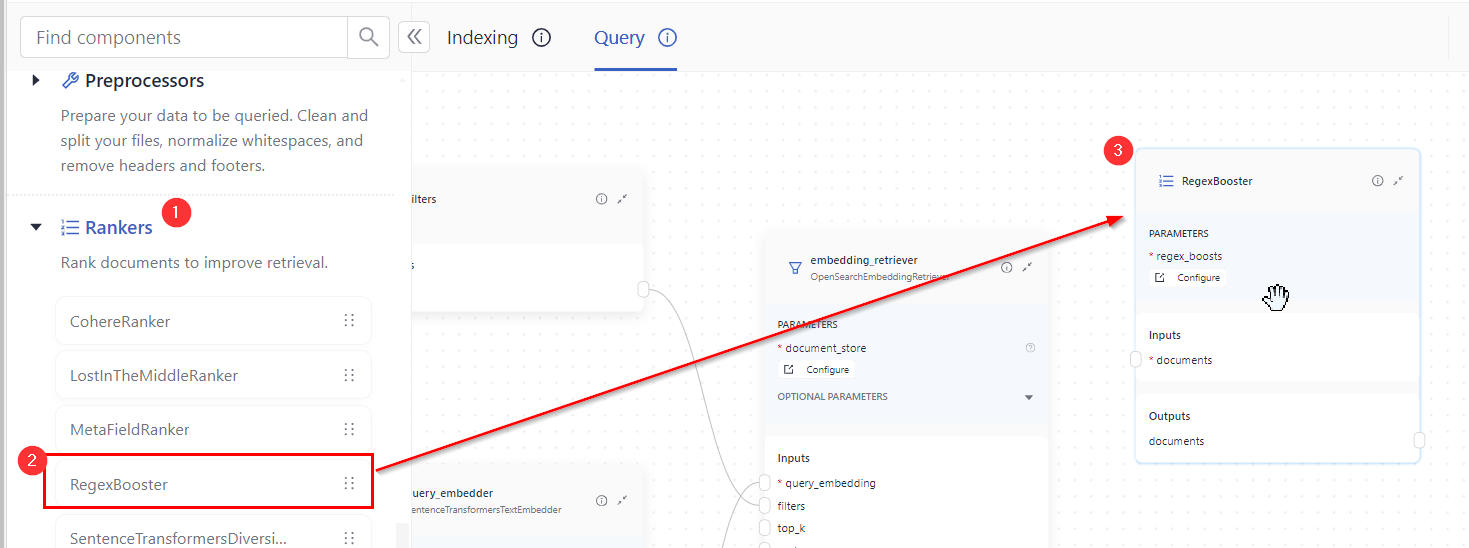
-
On the
RegexBoostercard, click Configure under theregex_boostsparameter and enter the following configuration:'\bcovid-19\b|\bcoronavirus\b': 2.0
'\bcancer\b': 1.5
'\basthma\b': 1.3
'\btreatment\b': 1.2
'\bsymptoms\b': 1.1 -
Draw a connection from
embedding_retriever's documents output toRegexBooster's documents input. -
Draw another connection from
RegexBooster's documents output toOutput's documents. This is what your canvas should look like: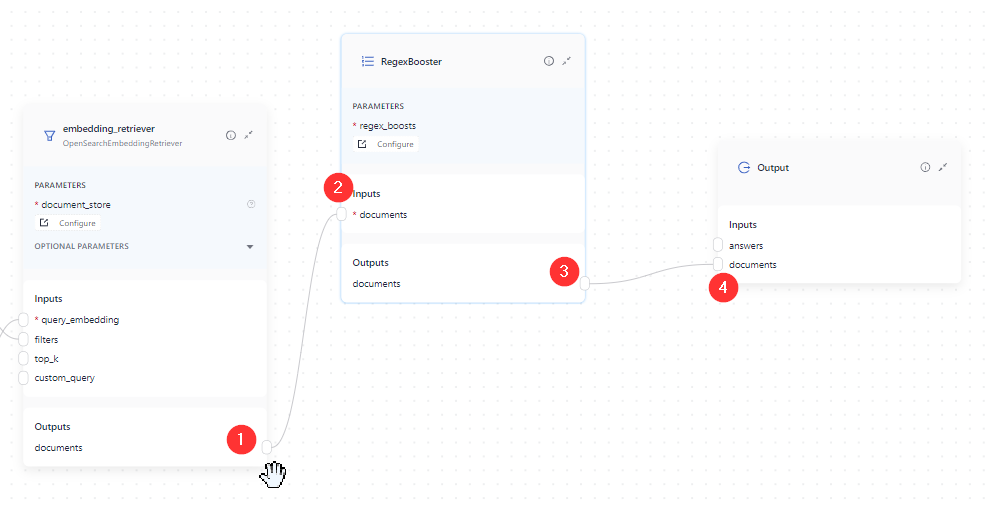
-
Save your pipeline.
-
Find
OpenSearchDocumentStoreamong your pipeline components. You'll notice it shows a warning that an index is missing. If you have an enabled index ready, select it, and go to the last step of this instruction. Otherwise, continue with the next step. -
Click the
indexfield and then click Create Index.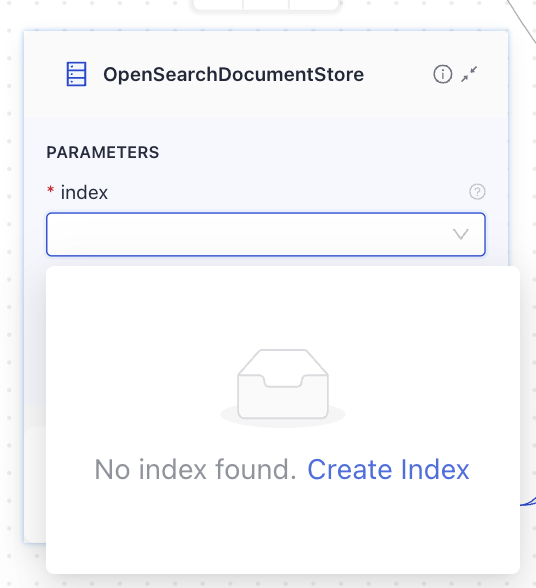
-
Choose the Standard Index (English) template, leave the default name, and click Create Index.
-
When you're redirected to Builder, click Enable in the top right corner. This indexes the files and makes them ready for search.

-
Go back to your query pipeline, open it for editing, and find the
OpenSearchDocumentStorecomponent. -
Click the index list on the component card and choose the Standard-Index-English index you just created.
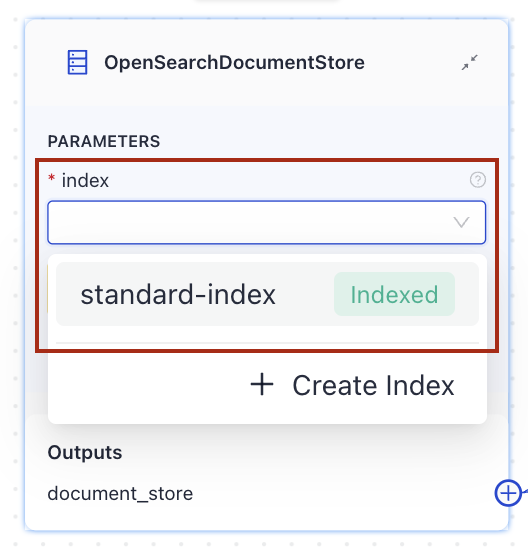
-
Save your changes and deploy the pipeline.
This is what your query pipeline should look like:
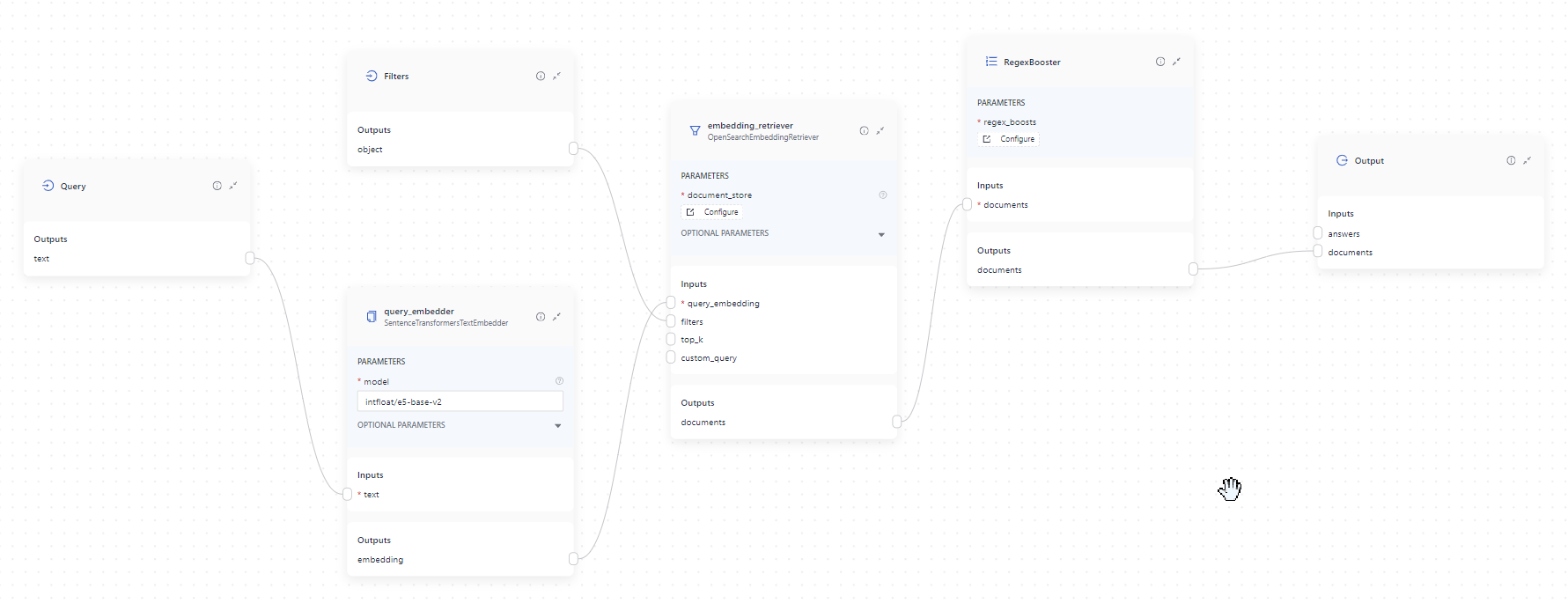
Use the code switcher in the upper right corner to switch to the YAML view. Here's the complete YAML configuration of your pipeline:
components:
query_embedder:
type: deepset_cloud_custom_nodes.embedders.nvidia.text_embedder.DeepsetNvidiaTextEmbedder
init_parameters:
normalize_embeddings: true
model: intfloat/e5-base-v2
embedding_retriever: # Selects the most similar documents from the document store
type: haystack_integrations.components.retrievers.opensearch.embedding_retriever.OpenSearchEmbeddingRetriever
init_parameters:
document_store:
type: haystack_integrations.document_stores.opensearch.document_store.OpenSearchDocumentStore
init_parameters:
hosts:
index: Standard-Index-English
max_chunk_bytes: 104857600
embedding_dim: 768
return_embedding: false
method:
mappings:
settings:
create_index: true
http_auth:
use_ssl:
verify_certs:
timeout:
top_k: 20 # The number of results to return
RegexBooster:
type: dc_custom_component.custom_components.rankers.regex_booster.RegexBooster
init_parameters:
regex_boosts:
\bcovid-19\b|\bcoronavirus\b: 2
\bcancer\b: 1.5
\basthma\b: 1.3
\btreatment\b: 1.2
\bsymptoms\b: 1.1
connections: # Defines how the components are connected
- sender: query_embedder.embedding
receiver: embedding_retriever.query_embedding
- sender: embedding_retriever.documents
receiver: RegexBooster.documents
inputs: # Define the inputs for your pipeline
query: # These components will receive the query as input
- "query_embedder.text"
filters: # These components will receive a potential query filter as input
- "embedding_retriever.filters"
outputs: # Defines the output of your pipeline
documents: "RegexBooster.documents" # The output of the pipeline is the retrieved documents
max_runs_per_component: 100
metadata: {}
Test the Pipeline with RegexBooster
Let's see if it works on real files.
-
Download this set of medical articles and extract it to your machine. You should have a set of 10 articles.
-
In Haystack Enterprise Platform, open the same workspace where you created the Semantic_Document_Search pipeline and go to Files.
-
Click Upload files, choose the files you extracted in step 1, and click Upload.
-
Let's create a document search pipeline without RegexBooster to compare the results:
- Go to Pipeline Templates.
- Choose Document Search templates, hover over Semantic Document Search, and click Use template.
- Change the pipeline name to
no_regexand click Create Pipeline. - Once you're redirected to Pipeline Builder, find
OpenSearchDocumentStoreand chooseStandard-Index-Englishas the index. If you used another index when creating the RegexBooster pipeline, choose the same index. - Save and deploy the pipeline.
-
When the pipeline is indexed, go to Playground and choose the Semantic_Document_Search pipeline.
-
In the Search field, type the following query:
Tell me about ongoing medical research. You can see that the top three documents are about coronavirus, cancer, and asthma. All of them are keywords RegexBooster prioritizes. -
Now, let's change the pipeline to the
no_regexone and repeat the same query. The top three documents are about Alzheimer, coronavirus, and cancer. The ranking of documents is different if we're not prioritizing certain keywords.
Congratulations!: You have implemented your custom component and imported it to Haystack Enterprise Platform. You can now run pipelines with RegexBooster!
Was this page helpful?